Template with Model Relations

When you want to display data from a model with a relationship, you need to slightly adjust how to write a template file.
Modal with ForeignKey
Showing data from a different model connected through ForeignKey is relatively straightforward.
In the ForeignKey (One-To-Many) case in the main figure, each employee data record has only one division data set. For example, John belongs to the Finance division but not to other divisions.
In this case, you can display data from the related model by connecting field names using . (dot).
For example, when you want to display the div_name field through the Employee model, you can describe it like {{ object.division.div_name }}. In this case, the object represents a record object in the Employee model.
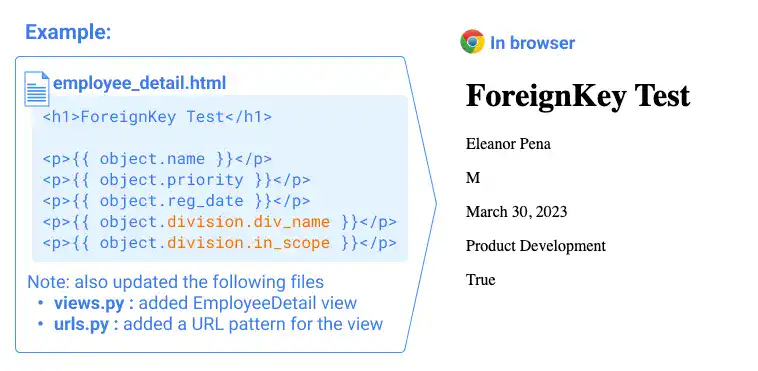
Below is an example of handling the template file for the model with ForeignKey.
Model with ManyToManyField
Showing data from a different model connected through ManyToManyField is slightly more complex. As the connected model may have multiple record objects, you need to iterate to deliver all record objects. For example, the Web Application Basic course may have multiple employees assigned.
To display ManyToMany Field, you need to do two things
- Use the
all()method to call theemployeeobject as aQuerySet - Use the
forstatement

Practice
Objective:
Learn how to handle ManyToManyField in the detail page template
In this practice, we'll show different codes for ManyToManyField in the detail page template and the corresponding results.
1. Without the all() method and the for statement
Open the course_detail.html file, add the yellow lines below, and save the file.
:
<p>Course Title : {{ course_object.title|upper }} </p>
<p>Level : {{ course_object.get_level_display }}</p>
<p>Assigned Employees : <p>
<p>{{ object.employee }}</p>
Go to one of the detail pages. You'll see that the browser doesn't show the employee data properly.

2. Only with the all() method
Change the code to the one below and check the detail page.
:
<p>Assigned Employees : <p>
<p>{{ object.employee.all }}</p>
Now, you can see that QuerySet is displayed, but not in the right format.

3. Only with the for statement
Change the code to the one below and check the detail page.
:
<p>Assigned Employees : <p>
{% for emp in object.employee %}
<p>{{ emp.name }} : {{ emp.division }}<p>
{% endfor %}
You will encounter an error saying 'ManyRelatedManager' object is not iterable. This means that Django expects an iterable object like QuerySet, but the data set is not iterable.

4. With both all() method and the for statement
Change the code to the one below and check the detail page.
:
<p>Assigned Employees : <p>
{% for emp in object.employee.all %}
<p>{{ emp.name }} : {{ emp.division }}<p>
{% endfor %}
Now, you can see that the data are properly displayed.

