SSL Setup – Certbot

SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a protocol used to establish secure and encrypted communication over the Internet. Most websites use the HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) protocol to increase their security level. SSL is necessary for the HTTPS protocol, which uses a combination of the standard HTTP protocol and the SSL protocol.
To establish SSL communication, the web server has to be certified by a certificate authority (CA). Let's encrypt is one of the CAs and provides SSL certificates for free. To obtain a Let's encrypt SSL certificate, Certbot is often used. It is free, open-source software that automates the process of obtaining and installing SSL certificates from Let's Encrypt.
SSL authentication mechanism
As explained, a prerequisite for establishing SSL communication is having a web server with an SSL certificate (SSL server). Here are the key processes of the SSL authentication mechanism:
- A client sends a request to the SSL server
- When the SSL server receives the request, the SSL server sends its SSL certificate with its public key to the client
- Once the client receives the SSL certificate and verifies it, the client creates a symmetric key and encrypts the symmetric key using the public key from the server
- Then, the client sends the encrypted symmetric key to the SSL server
- When the SSL server receives the encrypted symmetric key, the SSL server decrypts it with its own private key. By now, the client and the SSL server have the same symmetric key sent through a secured channel.
- Both use the symmetric key as a session key to create a secured communication channel
As you can see in the processes above, SSL uses both Asymmetric Encryption and Symmetric Encryption. SSL uses Asymmetric Encryption for the first authentication, which is more secure. For a session key, SSL uses Symmetric Encryption, which is faster.
How to set up SSL using Certbot
Certbot allows you to get an SSL certificate on your web server easily and quickly.
Here are the key steps:
- Install Certbot for Nginx on Ubuntu OS
- Open an SSL port
- Obtain an SSL certificate by running the certbot command
- Check the result and test the configuration
Install Certbot for Nginx on Ubuntu OS
Run the command below if you are using Nginx.
sudo apt-get install certbot python3-certbot-nginx
If you are using a different server, check the Certbot instruction page.
Open SSL port
By default, the SSL port (HTTPS port) is not open in AWS Lightsail. Go to the Lightsail console and check the Networking tab under the Ubuntu Instance.
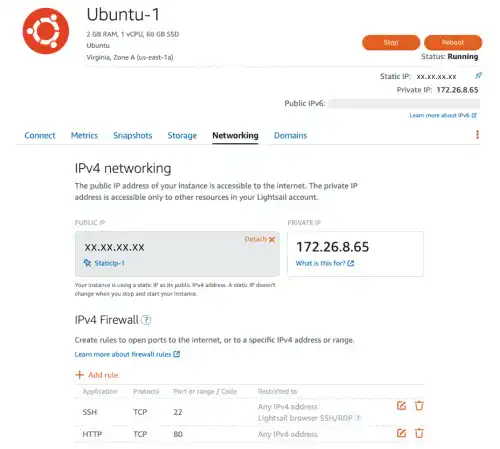
Select HTTPS and click on the Create button.
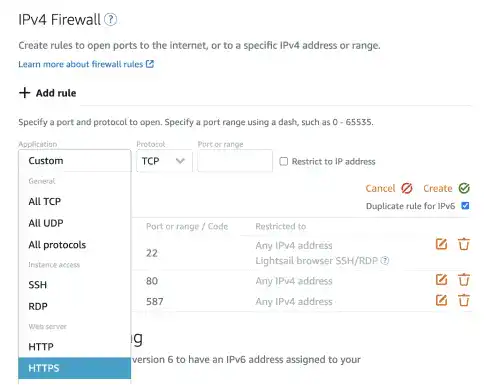
Now, the 443 port (for HTTPS) becomes open.
If you are also using UFW, check the status by running the ufw status command. 'Nginx Full' (or port 443) should be allowed for SSL communication.
sudo ufw status
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
22/tcp ALLOW Anywhere
Nginx Full ALLOW Anywhere
Obtain an SSL certificate by running the certbot command
Run the command below to obtain an SSL.
sudo certbot --nginx -d your_domain
When you run the command, several questions are asked. Here are the questions and answers for our case.
Your email
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx
Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): YOUR EMAIL
Terms of Services
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Please read the Terms of Service at
https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.3-September-21-2022.pdf. You must
agree in order to register with the ACME server at
https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
(A)gree/(C)ancel: A
You information disclosure
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier
Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit
organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work
encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
(Y)es/(N)o: N
Redirection of HTTP request
Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration.
2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for
new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this
change by editing your web server's configuration.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2
If the process is successful, you'll get the message like below.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://employee-learning.site
You should test your configuration at:
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=employee-learning.site
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/employee-learning.site/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/employee-learning.site/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2023-07-22. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again
with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of
your certificates, run "certbot renew"
- If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
Check the result and test the configuration
Check your site
Now you should be able to access your website with HTTPS protocol. Go to your URL that starts with https.
Test the configuration
You can also test the configuration at the URL in the success message like
'https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze...'.
It may take time to get the report. When the website is running properly in a secure condition, you'll see a report like the one below.
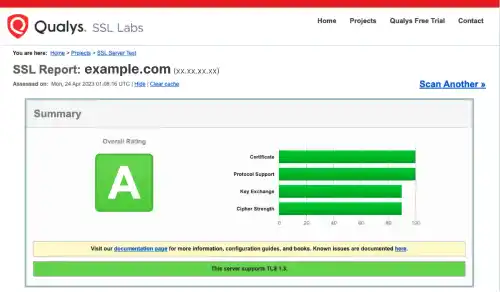
Check Nginx configuration
Certbot adds new settings in the Nginx configuration file for the project.
cat /etc/nginx/sites-available/project_d
You can see that the additional settings are made by Certbot.
:
listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
if ($host = your_domain) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
} # managed by Certbot
listen 80;
server_name xx.xx.xx.xx your_domain;
return 404; # managed by Certbot
Test automatic renewal
According to the Certbot instructions, the Certbot packages on your system come with a cron job or systemd timer that will renew your certificates automatically before they expire.
You can test automatic renewal by running the command below.
sudo certbot renew --dry-run
If the dry-run is successful, you'll see a success message like the one below.
:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
** DRY RUN: simulating 'certbot renew' close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates below have not been saved.)
Congratulations, all renewals succeeded. The following certs have been renewed:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain/fullchain.pem (success)
** DRY RUN: simulating 'certbot renew' close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates above have not been saved.)
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
:
For more details, check certbot instructions.

