margin: auto

Unlike for padding, you can use auto as a keyword for the margin property value. When you use auto, the browser tries to maximize margins as much as possible.
For example, in the case like in the illustration below,
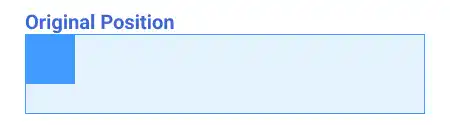
when you set margin: auto for the child element, the auto value tries to maximize the margin for both sides. As a result, the child element is placed in the center of the parent element horizontally.

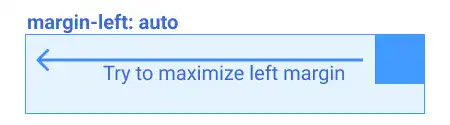
When you set margin-left: auto for the child element, the auto value tries to maximize the left side of the margin. As a result, the child element is pushed to the right edge of the parent element.
 margin: auto with Flex Box
margin: auto with Flex Box
In the regular situation, margin: auto works only horizontally; however, when the parent element is set as a Flex Box, the auto keyword works for both horizontal and vertical dimensions. We'll explain how margin: auto works with Flex Box later.


