Buttons

There are several approaches to creating buttons using different tags (<a>, <button>, <input>). Functionalities are different by tag; but by customizing CSS, you can achieve the same style regardless of your tag choices.
1. Buttons with the <a> tag
Using the <a> tag is the simplest approach to creating a button. This approach can be used when you want to create a button to add a link to another page; however, you cannot use this approach for the button used to submit form data. As the <a> tag has an end tag, you can insert an icon into the button design.
Syntax
You can use the syntax below. Add a class for the button styling. You can use any class name. "btn" is often used for the button class name. To open the link in a different tab, you can also add the target="_blank" attribute.

Styling
To style a button, you need to define many properties:
- For background and border design
background-colorborder(style, width, color)border-radius
- For text design
colorfont-sizefont-familyline-heighttext-decoration)
- For size, spacing, and layout
heightwidthpaddingmargindisplay(including related properties)
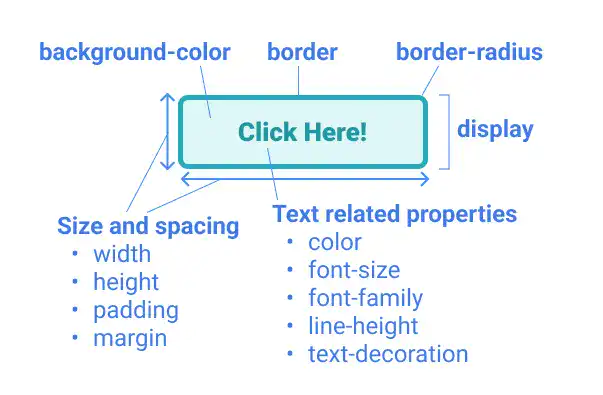
You can decide background-color, border and border-radius flexibly based on your design choice; however, you may need to carefully manage text, size, spacing, and layout-related properties as they are important to organize the button design structure.
Text related property
color, font-size and font-family are straightforward. You can decide based on your design choice; however, you need to pay attention to text-decoration and line-height.
As the <a> tag shows underline by default, usually, you want to set text-decoration: none to remove the underline.
The line-height property is used to adjust the vertical position of the text. We usually set the same height as the height of the button so that you can place the text in the center vertically. When you use Flex Box approach explained below, you don't need to set line-height as you need to adjust text position using the align-content property.
Size, spacing, and layout-related property
As <a> is an inline element, you cannot set its sizes. To set sizes, you need to change the display property. Usually, there are two ways to do it.
Flex Box
You can use Flex Box to style buttons. In this approach, you need to set display: flex at both the parent element and the <a> element. You can also adjust the position of the button using justify-content in the parent element.
To adjust the text position in a button, you can use justify-content and align-items in the <a> element itself.
Here is an example of the code for a button using the Flex Box approach with the <a> tag. To add a hyperlink, you can replace the # part with a URL.
<!--HTML-->
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: center;">
<a href="#" class="btn-flex">Click Here!</a>
</div>
<!--CSS-->
<style>
.btn-flex{
background-color:#2197A2;
color: white;
border-style: none;
border-radius: 25px;
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
font-size: 1.5rem;
font-family: roboto, sans-serif;
text-decoration: none;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
</style>
Inline-blok
Using flex: inline-block at the <a> element level is another approach. In this case, you don't need to set the flex property at the parent level but you may need to set text-align to define the position of the button.
For the alignment of the position of the text in a button, you can use text-align for the horizontal position and line-height for the vertical position. To place the text in the center vertically, you can use the same height as the height of the button.
Here is an example of the code for a button using the inline-block approach with the <a> tag.
<!--HTML-->
<div style="text-align: center;">
<a href="#" class="btn-inline-block">Click Here!</a>
</div>
<!--CSS-->
<style>
.btn-inline-block{
background-color: #2197A2;
color: white;
border-style: none;
border-radius: 25px;
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
font-size: 1.5rem;
font-family: roboto, sans-serif;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
text-align: center;
line-height: 50px;
}
</style>
2. Buttons with the <button> tag
For the buttons to handle forms, you can use the <button> tag. You can also use the <button> tag to set a hyperlink but this approach is different from the one of the <a> tag.
Syntax
The syntax of the <button> tag is slightly more complicated than that of the <a> tag. To add a hyperlink, you need to use the onclick attribute like in the example below.

Styling
Unlike the <a> tag, you can set the width and height for the <button> tag; however, using the Flex Box approach may be easier to style buttons with the <button> tag. As there is no default underline in the <button> element, you don't need to set text-decoration: none.
Here is an example of the code for a button that uses the <button> tag approach.
<!--HTML-->
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: center;">
<button onclick="location.href=`#`" class="btn">Here!</button>
</div>
<!--CSS-->
<style>
.btn{
background-color:#2197A2;
color: white;
border-style: none;
border-radius: 25px;
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
font-size: 1.5rem;
font-family: roboto, sans-serif;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
</style>
3. Buttons with the <input> tag
For the buttons to handle forms, you can also use the <input> tag. As the <input> tag doesn't have the end tag, you cannot nest the <img> element to insert an icon. The <input> tag was commonly used before the <button> tag was introduced; however, as you can achieve the same results using the <button> tag, it is better to use the <button> tag.
Syntax
As there is no end tag, you need to put the text in the button using the value attribute.

Styling
You can use the same approach to styling as the one used for the <button> element styling.
Practice
Objective:
Create and style buttons with different approaches
1. Create a new HTML file for this chapter
- Create a copy of the chapter16.html file and change the name to chapter17.html.
- Change the
<title>section to 17. Creating and Styling Components. - Also, delete the existing content of the
<body>element that was created in the previous chapter. - Add the
<h1>tag to show the chapter title of this page at the top of the page. - The code should look like the one below.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<!--Google Font-->
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com">
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.gstatic.com" crossorigin>
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Roboto:ital,wght@0,100;0,300;0,400;0,500;0,700;0,900;1,100;1,300;1,400;1,500;1,700;1,900&display=swap" rel="stylesheet">
<!--Custom CSS-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/practice.css">
<title>17. Creating and Styling Components</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Chapter 17. Creating and Styling Components</h1>
</body>
</html>
2. Update the body section
Add the code below in the <body> section of the HTML file. We are creating seven sets of buttons with different approaches.
- Using the
<a>tag with Flex Box - Using the
<a>tag with Inline-block - Using the
<button>tag with Flex Box - Using the
<input>tag with Flex Box - Adjusting colors with a white background
- Adjusting size to make a smaller button
- Adjusting shape to create a previous button and a next button
<h2 style="text-align: center;">Buttons</h2>
<p style="text-align: center;">The a tag with Flex Box</p>
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: center; padding-bottom: 20px;">
<a href="main-page.html" class="btn-flex">Button 1</a>
</div>
<p style="text-align: center;">The a tag with Inline-block</p>
<div style="text-align: center; padding-bottom: 20px;">
<a href="main-page.html" class="btn-inline">Button 2</a>
</div>
<p style="text-align: center;">The button tag with Flex Box</p>
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: center; padding-bottom: 20px;">
<button onclick="location.href=`main-page.html`" class="btn-flex">Button 3</button>
</div>
<p style="text-align: center;">The input tag with Flex Box</p>
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: center; padding-bottom: 20px;">
<input type="button" onclick="location.href=`main-page.html`" value="Button 4" class="btn-flex">
</div>
<p style="text-align: center;">White background</p>
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: center; padding-bottom: 20px;">
<a href="main-page.html" class="btn-white-bg">Button 5</a>
</div>
<p style="text-align: center;">Small size</p>
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: center; padding-bottom: 20px;">
<a href="main-page.html" class="btn-small">Button 6</a>
</div>
<p style="text-align: center;">Custom shapes</p>
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: center; padding-bottom: 20px;">
<div class="btn-group">
<a class="btn-previous">←</a>
<a class="btn-next">→</a>
</div>
</div>
<hr>
3. Create a new CSS file for component styling and add code
Create a component.css file and add new code for styling the buttons.
/* Chapter 17. CSS: Styling Components */
/* Buttons */
.btn-flex{
background-color:#2197A2;
color: white;
border-style: none;
border-radius: 25px;
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
font-size: 1.5rem;
font-family: roboto, sans-serif;
text-decoration: none;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.btn-inline{
background-color:#2197A2;
color: white;
border-style: none;
border-radius: 25px;
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
font-size: 1.5rem;
font-family: roboto, sans-serif;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
text-align: center;
line-height: 50px;
}
.btn-white-bg{
background-color:white;
color: #2197A2;
border: solid 2px #2197A2;
border-radius: 25px;
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
font-size: 1.5rem;
font-family: roboto, sans-serif;
text-decoration: none;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.btn-small{
background-color:#2197A2;
color: white;
border-style: none;
border-radius: 15px;
width: 150px;
height: 30px;
font-size: 1rem;
font-family: roboto, sans-serif;
text-decoration: none;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.btn-group{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
list-style: none;
gap: 5px;
}
.btn-previous{
background-color:#2197A2;
color: white;
border-style: none;
width: 60px;
height: 25px;
font-size: 1rem;
font-family: roboto, sans-serif;
border-radius: 25px 0px 0px 25px;
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
line-height: 25px;
}
.btn-next{
background-color:#2197A2;
color: white;
border-style: none;
width: 60px;
height: 25px;
font-size: 1rem;
font-family: roboto, sans-serif;
border-radius: 0px 25px 25px 0px;
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
line-height: 25px;
}
4. Check the result with a browser
Open chapter17.html with a browser. You can see various button designs.
You can also check the sample result here (Demo Site).

