margin

Margin sets space between objects. Similarly to padding, margin is very important for design layout.
Length and keyword
You can specify a margin size using one of the length units or keywords. The default margin value is 0. You can use the auto keyword, which is useful for block element layout. We'll explain how to use auto later.
Length unit
pxemrem%vwvh
Keyword
autoinitialinherit
Margins for block elements and inline elements
Like padding, behaviors of margin can differ by type of element. You can set margins for block elements horizontally and vertically; however, you cannot set vertical margins for inline elements.
Practice 1
Objective:
Test margins for block elements and inline elements
1. Update the body section of the HTML file
Add the code below to the chapter10.html file. The <br> tag between the <a> element and the <span> element is used for checking how margins for inline elements are applied vertically.
<h2>Margin</h2>
<div class="size-object" style="margin:initial">div element: Original</div>
<div class="size-object" style="margin:30px">div element: margin 30px</div>
<p class="size-object" style="margin:initial">p element: Original</p>
<p class="size-object" style="margin:30px">p element: margin 30px</p>
<a class="size-object" style="margin:initial">a element: Original</a>
<a class="size-object" style="margin:30px">a element: margin 30px</a>
<br>
<span class="size-object" style="margin:initial">span element: Original</span>
<span class="size-object" style="margin:30px">span element: margin 30px</span>
<hr>
2. Check the result with a browser
- Open chapter10.html with a browser.
- You can see how each element is displayed. From this, you can understand:
- The default
marginis zero. - You can set a
marginfor the block elements horizontally and vertically; however, vertical margins for the inline elements are not applied.
- The default
You can also check the sample result here (Demo Site).
Margin overlap
margin vs. margin
When two elements with margins are placed side by side, their margins overlap. In this situation, a margin with a larger value will be applied to the margin between the two elements.
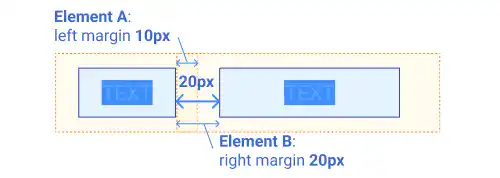
In the illustration below, element A has a right margin of 10px while element B has a left margin of 20px. In this case, the margin between the two becomes 20px.
Margins don't overlap paddings
One potential question about margins and paddings is if margins overlap paddings.
The answer is no. Even though a block element with a margin is nested under a parent block element with paddings, both settings are applied.
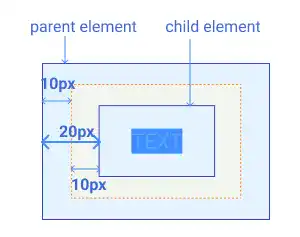
In the example below, the parent element has 10px of padding while the child element has 10px of margin. In this case, the distance between the parent element's borderline and the child element's borderline becomes 20px.
Practice 2
Objective:
Check margin overlaps
1. Update the body section of the HTML file
Add the code below to the chapter10.html file.
<h2>Margin: Overlap</h2>
<div class="size-object" style="height:30px; margin:30px">height:10px; margin:10px</div>
<div class="size-object" style="height:30px; margin:30px">height:10px; margin:10px</div>
<div class="size-object" style="height:30px; margin:30px">height:10px; margin:10px</div>
<hr>
<h2>Margin: Child Margin and Parent Padding</h2>
<div class="size-object" style="width:300px; padding:30px">
<div class="size-child-object" style="height:30px; margin:30px; border: 1px dotted">hight:30px; margin: 30px</div>
</div>
<hr>
2. Check the result with a browser
- Open chapter10.html with a browser.
- You can confirm two things:
- In the first example, the gaps between all the elements stay the same as the elements' height (20px) although each element has 20px of margins. This means margins overlap.
- In the second example, the child element's margin and the parent element's padding are both 20px, resulting in a 40px gap between the child's border and the parent's border. This means there is no overlap between margin and padding.

You can also check the sample result here (Demo Site).
Margins with multiple values
You can set different margin sizes for different sides of an element. The approach is the same as the one for padding.
1 value (all sides)
When you specify only one margin value, the value is applied to all sides of the element.
2 values (top and bottom vs. right and left)
When you specify two margin values, the first value is applied to the top and bottom margins, while the second value is applied to the right and left margins.
3 values (top vs. right and left vs. bottom)
When you specify three margin values, the first value is applied to the top margin, the second value is applied to the right and left margin, and the last value is applied to the bottom margin.
4 values (clockwise order from the top)
When you specify four margin values, the value is applied from the top in the clockwise order (the order of top, right, bottom, and left).
Practice 3
Objective:
Test margins with multiple property values
1. Update the body section of the HTML file
Add the code below to the chapter10.html file. We are using display: inline-block to show the results clearly. We'll explain about the display property later in this course. For now, just copy and paste the code.
<h2>Margin: multiple values</h2>
<div class="size-object" style="display:inline-block">
<div class="size-child-object" style="width:200px;">Before padding</div>
</div>
<div class="size-object" style="display:inline-block">
<div class="size-child-object" style="width:200px;margin: 10px;">Margin 10px</div>
</div>
<div class="size-object" style="display:inline-block">
<div class="size-child-object" style="width:200px;margin: 5px 10px;">Margin 5px 10px</div>
</div>
<div class="size-object" style="display:inline-block">
<div class="size-child-object" style="width:200px;margin: 5px 10px 1px;">Margin 5px 10px 1px</div>
</div>
<div class="size-object" style="display:inline-block">
<div class="size-child-object" style="width:200px;margin: 5px 10px 1px 2px;">Margin 5px 10px 1px 2px</div>
</div>
<hr>
2. Check the result with a browser
- Open chapter10.html with a browser.
- You can see that values are applied in different ways depending on how many values you set for margins.
You can also check the sample result here (Demo Site).
Note: Margin of <body>
Although the default margin value is usually zero, the body element has a pre-set margin depending on the browser. You can see that there is a space like in the image below.

Depending on your website design, you may not want to have a gap at the edge of the browser. In that case, you need to set margin:0 in the body element. You can stretch out elements from the left edge of the browser to the right edge as shown below.






