font-weight and font-style

The font-weight property is used to set the thickness of fonts. The font-style is used to set italic or oblique font.
font-weight
You can specify font-weight with weight numbers or keywords.
Weight numbers
For numbers, you can select from nine sets of numbers from 100 to 900. The smaller the number, the thinner the font becomes. When you specify a number, you need to make sure that the font with the specified weight is available. If the specified weight is not available, a browser chooses an alternative.
Keywords
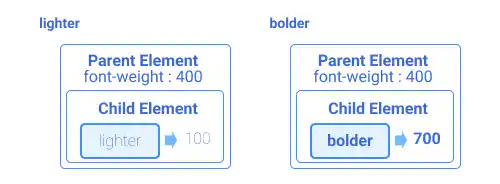
The default is normal which is equivalent to 400 font weight. bold is equivalent to 700 weight. You can use lighter or bolder fonts. Actual weights selected with those keywords depend on the parent font-weight. If you use lighter, a browser finds a font thinner than the parent's font. If you use bolder, a browser finds a font thicker than the parent's font.
 <b> and <strong> tag
<b> and <strong> tag
Bold can also be implemented directly by HTML. The <b> tag is used to simply bold the selected part without adding any meaning. The <strong> tag has a semantic to stress that the selected part is important for the page.
Practice 1
Objective:
Test different font weights
1. Update the body section of the HTML file
Add the code below at the end of the <body> section in the chapter11.html file. In this code, we are listing all weight numbers and keywords.
<h2>Font Weight</h2>
<p>Font Weight: Original</p>
<p style="font-weight: 100;">Font Weight: 100</p>
<p style="font-weight: 200;">Font Weight: 200</p>
<p style="font-weight: 300;">Font Weight: 300</p>
<p style="font-weight: 400;">Font Weight: 400</p>
<p style="font-weight: 500;">Font Weight: 500</p>
<p style="font-weight: 600;">Font Weight: 600</p>
<p style="font-weight: 700;">Font Weight: 700</p>
<p style="font-weight: 800;">Font Weight: 800</p>
<p style="font-weight: 900;">Font Weight: 900</p>
<p style="font-weight: lighter;">Font Weight: lighter</p>
<p style="font-weight: bolder;">Font Weight: bolder</p>
<p style="font-weight: bold;">Font Weight: bold</p>
<hr>
2. Check the result with a browser
- Open chapter11.html with a browser.
- Although Roboto fonts we set exclude
200,600,and800weights, the browser renders those elements using alternative font weights. (200,600,and800are replaced with100,700,and900respectively in this case.)
You can also check the sample result here (Demo Site).
font-style
font-style is primarily used to change font style to italic or oblique. Oblique is a font style slightly inclined to the right based on a regular font. The italic font looks very similar to the oblique font; however, some design adjustments are added to the italic font. Practically, you can choose italic or oblique based on font availability.
Keywords
The default is normal. You can use italic for italic font style and oblique for oblique font style.
 <i> and <em> tag
<i> and <em> tag
Italic font can also be implemented directly by HTML. The <i> tag is used to simply change the selected part to italic without adding any meaning. The <em> tag has a semantic to stress that the selected part is important for the page.
Practice 2
Objective:
Try to set italic fonts using various approaches.
1. Update the body section of the HTML file
Add the code below at the end of the <body> section in the chapter11.html file. In this code, we are changing fonts to italic using CSS (the font-style property) and HTML (the <i> tag and <em> tag).
<h2>Font Style</h2>
<p style="font-weight: 400; font-style: italic;">Font Weight & Style: 400 Italic (CSS)</p>
<p style="font-weight: 400;">
<i>Font Weight & Style: 400 Italic (HTML i tag)</i>
</p>
<p style="font-weight: 400;">
<em>Font Weight & Style: 400 Italic (HTML em tag)</em>
</p>
<hr>
2. Check the result with a browser
- Open chapter11.html with a browser.
- You can see that the different sets of code provide the same results.
You can also check the sample result here (Demo Site).





