font-family

The font-family property is used to set font families are applied to the web page. You can set multiple font families, so that a browser can render alternative font families when a specific font is not available on a certain device.
Deciding which font family or typeface is one of the most important design aspects of website design. As there are many font families available, you need to carefully select the font families you want to use on your website.
Font Family
The font family is a collection of fonts that are designed under a common design theme. Each font family has a different font weight (e.g., thin, regular, bold) and italic font, etc.
Font families can be categorized under generic families which are related to the origin of each font family. For example, Serif, Sans-Serif, and Monospace are frequently used generic families. Each has unique design aspects.
Serif
Serif font families tend to have finishing strokes and create a traditional impression. Some examples of such font families are Times New Roman, Georgia, and Garamond.
Sans-Serif
Sans-Serif font families are plain at the end of strokes and create a more modern impression. Some examples of such font families are Helvetica, Arial, and Verdana.
Monospace
The criterion of a monospace font is that each letter has the same fixed width. The monospace fonts are often used to set samples of computer code. Some examples of such font families are Monaco, Courier and Menlo.
font-family property setting
Fonts on websites are a user's computer dependent. Your selected font may not be rendered properly in website viewers' browsers if the font is not available in their browser. To avoid rendering very different fonts, when you set the font-family property, you need to specify multiple font families followed by a generic family.
A browser tries to render fonts using the first font family specified. If the font family is not available, the browser tries the next one. Generic font families are a fallback mechanism. If none of the specified fonts can be rendered, the browser picks a similar font in the generic family.
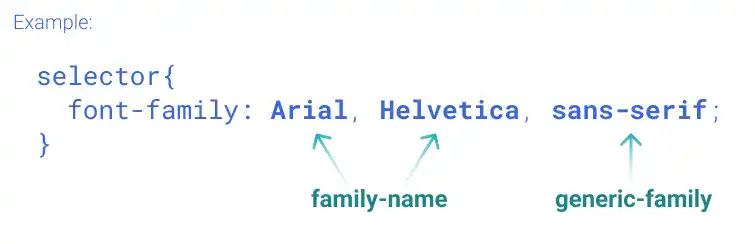
 Font family name with space
Font family name with space
If the font name has a space such as Times New Roman, you need to use single quotes like 'Times New Roman'.
Practice
Objective:
Set several font families
1. Update the body section of the HTML file
Add the code below at the end of the <body> section in the chapter11.html file. In this code, we are setting different font families for each paragraph for practice purposes. (Usually, font families are set at the body element level.)
<h2>Font Family</h2>
<p>1. Font Family: Original</p>
<p style="font-family: serif;">2. Font Family: Serif</p>
<p style="font-family: roboto;">3. Font Family: Roboto</p>
<p style="font-family: roboto, sans-serif;">4. Font Family: Roboto, Sans-Serif</p>
<p style="font-family: monospace;">5. Font Family: monospace</p>
<hr>
2. Check the result with a browser
- Open chapter11.html with different browsers.
- These are the examples rendered in Chrome and Safari. Results can be different as each device has different fonts installed. In the case examples below, you can see several things:
- 1st and 2nd case: From these cases, you can see that the default font is Serif.
- 3rd case: As Safari doesn't have Roboto font as the default setting, it renders its default font family, which is Serif. (Note: In any case, if you have Roboto font installed on your computer, the font can be rendered properly even in Safari.)
- 4th case: Safari renders a font similar to Roboto as Sans-Serif is specified as a generic font family.
- 5th case: Chrome and Safari use different monospace fonts.
Here are the output examples:
With Chrome

With Safari






