Django Models – Help Text Option

Using the help_text field option, you can add a help text message in the Django admin site for the field. Its execution is straightforward. Add the help_text option with a text message you want to show.
Practice
Objective:
Add a new field in an existing model after data entry
As we already added some data in the models, when we add new fields in the existing model, we need to consider how to handle the missing data for the new fields in the existing model.
In this practice, we'll explain how to handle it while implementing the help_text option.
1. Edit models.py
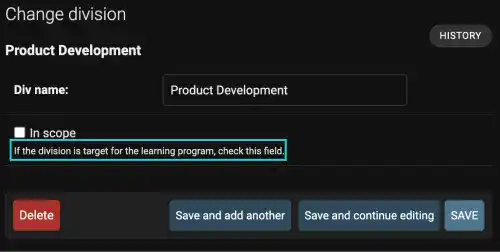
Edit the Division model by adding a new field named in_scope. This field is expected to be used to select the target division of the digital skill learning program. Use the BooleanField with the help_text option. Edit the models.py file by adding the yellow line, as shown below.
class Division(models.Model):
div_name=models.CharField(max_length=25)
in_scope=models.BooleanField(help_text="If the division is target for the learning program, check this field.")
def __str__(self):
return self.div_name
2. Run the makemigrations command
Run the makemigration command.
python manage.py makemigrations employee_learning
You'll see an alert message saying, "...impossible to add a non-nullable field 'in_scope' to division without specifying a default...". This is because the data for the new field of the existing records are missing.
It is impossible to add a non-nullable field 'in_scope' to division without specifying a default. This is because the database needs something to populate existing rows.
Please select a fix:
1) Provide a one-off default now (will be set on all existing rows with a null value for this column)
2) Quit and manually define a default value in models.py.
Select an option:
Answer 1 at this time. Then, the prompt will ask what data should be filled in.
Select an option: 1
Please enter the default value as valid Python.
The datetime and django.utils.timezone modules are available, so it is possible to provide e.g. timezone.now as a value.
Type 'exit' to exit this prompt
>>>
As the field type of the in_scope field is Boolean, type "False". You'll see that a new migration file is created.
>>> False
Migrations for 'employee_learning':
employee_learning/migrations/0003_division_in_scope.py
- Add field in_scope to division
3. Run the migrate command
Finally, run the migrate command.
python manage.py migrate
You'll see that the migration is successfully completed.
Operations to perform:
Apply all migrations: admin, auth, contenttypes, employee_learning, sessions, test_app
Running migrations:
Applying employee_learning.0003_division_in_scope... OK
4. Check the Django admin site
Go to localhost:8000/admin/. Open one of the records of the Division model. You can see that the in_scope field with the helping text message has been added to the Division model. Also, the checkbox is not checked, as we put "False" as the default value for existing records.