Django Allauth (6) – Social Login with Google

This lesson will explain how to set up a social login with Google.
Note: The approach can change depending on Google's policy.
1. Register a new OAuth app in the GCP(Google Cloud Platform) console
Go to the GCP (Google Cloud Platform). Click on the Console button on the top bar.
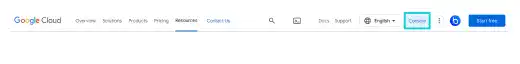
Click on Select a project. And press the NEW PROJECT button.
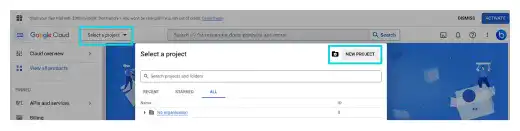
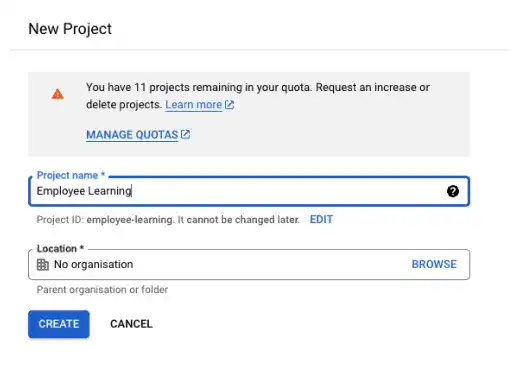
Add a project name (e.g., Employee Learning) and press the CREATE button.
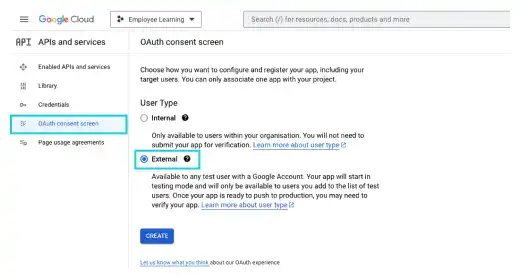
In the created project (Employee Learning), select API and services. Click on OAuth consent screen.
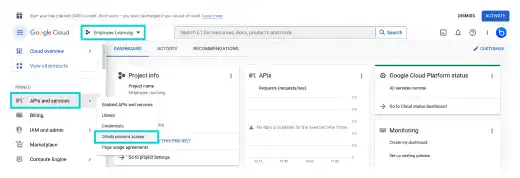
On the OAuth consent screen, select External and press the CREATE button.
Add App name, User support email, and Developer contact information at the bottom.
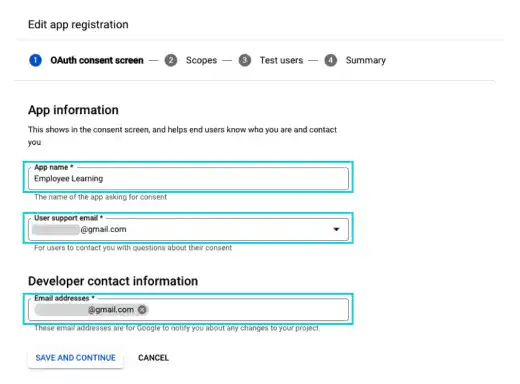
There is no need to add other information. Click on Save And Continue in the rest of the steps.
Once the OAuth consent part is done, select Credentials on the left sidebar. And click on + CREATE CREDENTIALS. Select OAuth client ID from the dropdown menu.
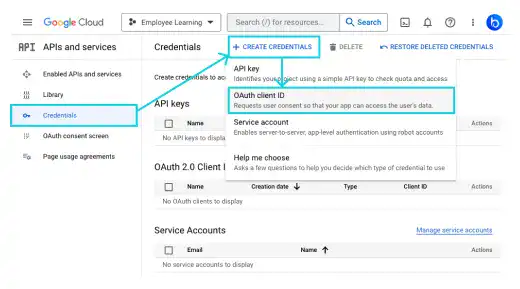
Add the following information.
- Application Type: Web application
- Name: Any name (e.g., Employee Learning)
- Authorized JavaScript origins: http://localhost:8000
- Authorized redirect URIs: http://localhost:8000/accounts/google/login/callback/
Carefully type, especially for Authorized JavaScript origins and Authorized redirect URIs.
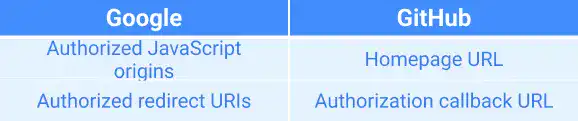
- Authorized JavaScript origins is the Homepage URL in GitHub.
- Authorized redirect URIs is Authorization callback URL in GitHub.
Often, error come from this setting. If you are using 127.0.0.1 for the runserver command, use 127.0.0.1 here as well. Another point you need to be careful about is the accounts part. Don't forget to put s at the end.
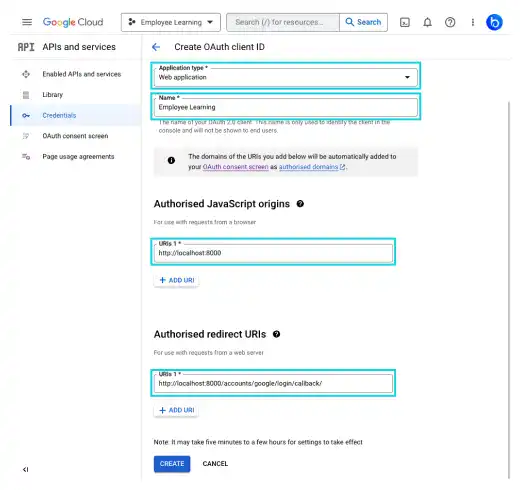
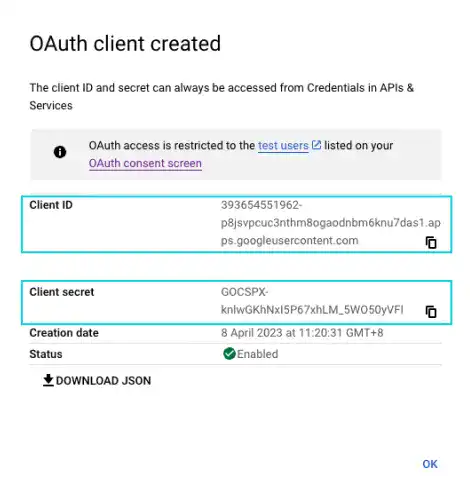
Once you have filled in all the required data, click on CREATE. You can see a pop-up with the Client ID and Client secret and save them somewhere in a safe place. We'll use them later.
2. Edit settings.py
To add the Google social login feature, you need to edit settings.py.
- Add
allauth google appin theINSTALLED_APPSsection - Add
SCOPEand other settings underSOCIALACCOUNT_PROVIDERS
INSTALLED_APPS = [
:
'allauth.socialaccount.providers.github',
'allauth.socialaccount.providers.google',
]
###Social Login###
SOCIALACCOUNT_PROVIDERS = {
'github': {
'SCOPE': [
'user',
'repo',
'read:org',
],
},
'google': {
'SCOPE': [
'profile',
'email',
],
'AUTH_PARAMS': {
'access_type': 'online',
},
'OAUTH_PKCE_ENABLED': True,
},
}
Check the allauth official document for details.
3. Register in Django Admin
As the last step, you need to add your domain on the Site page and Google social login settings on the Social applications page in the Django admin site.
Update the domain information on the Site page
You can skip this step if you have done this in the previous GitHub section.
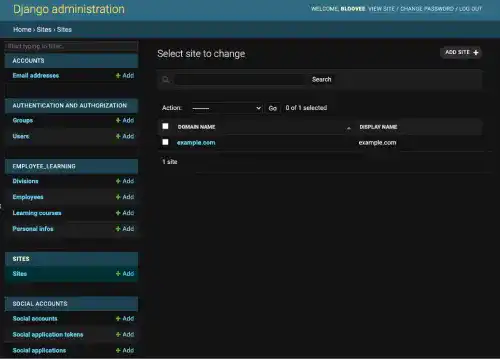
Click on the Site link on the left sidebar. As a default, example.com is registered on the Site page.
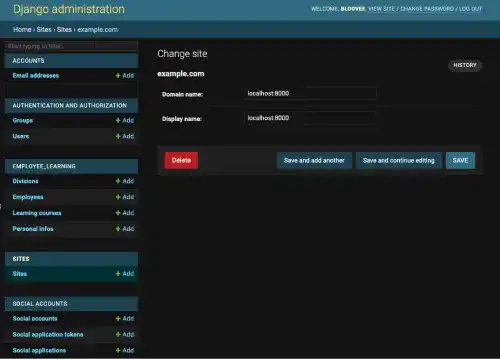
Change it to localhost:8000.
Add Google social login settings on the Social applications page
Click on the +Add button beside the Social applications link on the left sidebar.
Add the following settings:
- Provider: GitHub
- Name: Any name
- Client ID: Client ID obtained from GitHub website
- Secret Key: Client secret obtained from GitHub website
- Sites: localhost:8000
Once it's done, save the record.
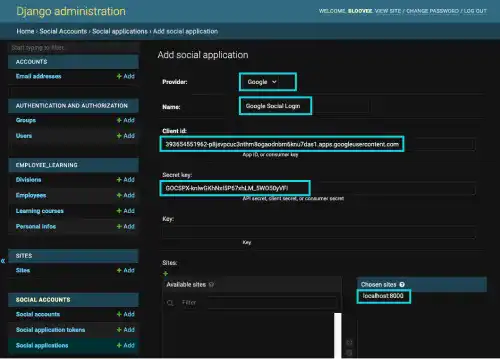
Once it's done, save the record.
4. Check the results
Go to the Sign In (Login) page (not the Sign Up page!) to check the results.
You can see the link named Google.
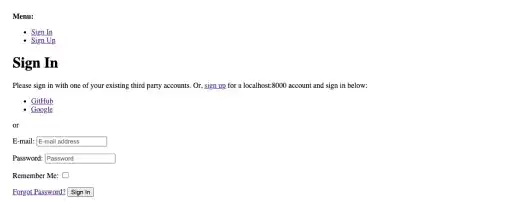
Click on the link. And then click on the continue button.

You'll be redirected to the Google's site. Select an account you want to use for the social login.
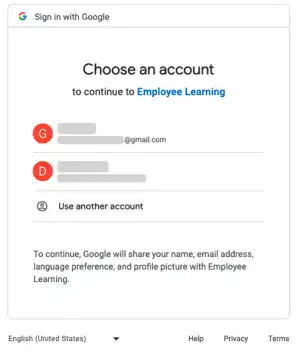
Once you select an account, you'll jump to the landing page (You are successfully logged in to the app).
Unlike with the GitHub social login setting, you don't need to verify your email again.

