Standard Input Output and Redirection

Standard Input, Output and Error Output
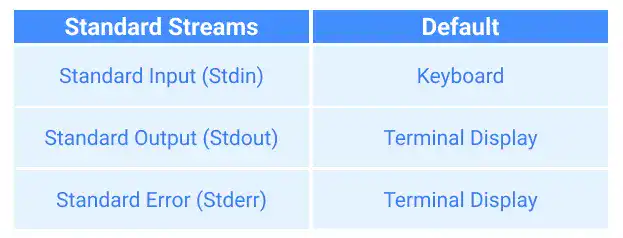
In general, computer commands or programs process input and generate output. Standard input and output define where data come from and where processed data go to.
Standard Input (Stdin)
Standard input defines where input data comes from. Linux OS's preset standard input is generally the keyboard. When you type in the command line, the typed string becomes the input of the command.
Standard Output (Stdout)
Standard output defines where output data are generated. Linux OS's preset standard output is generally command-line (terminal).
Standard Error (Stderr)
Linux OS's preset standard error output is generally command-line (terminal).
Here is the summary of the above.
Redirection
Redirection is used to change Stdin, Stdout, or Stderr. In programming, the most frequently used redirection option is redirection via a text file.
Redirection of stdin (<)
To redirect standard input, use < after a command followed by new standard input.

For example, if you want to sort the file_a contents, run the command below.
sort < file_a
Redirection of stdout (> or >>)
To redirect standard output, use > or >> after a command followed by a new standard output.
When you use >, the output will overwrite the existing contents while when you use >>, the output will be added at the end of the existing contents.

For example, run the following command to save the output of the ls command for the / (root) directory in the list.txt file. To avoid a permission error, run the command as the superuser.
sudo su
ls / > list.txt
You can see that the list of directories and files under the / (root) directory is saved in the file.
cat list.txt
bin
boot
dev
:
Following the above process, run the two commands. One is to list directories and files of the /usr directory with > and the other is to list the same directory with >>.
First, run the command with >> shown below. You can see that the list of the /usr directory is added after the /(root) directory list.
ls /usr >> list.txt
cat list.txt
bin
boot
dev
etc
home
lib
lib32
lib64
libx32
lost+found
:
bin
games
include
lib
lib32
lib64
libexec
libx32
local
sbin
share
src
Next, run the same command but with > like shown below. You can see that the list of the /usr directory overwrote the original content of the file.
ls /usr > list.txt
cat list.txt
bin
games
include
lib
lib32
lib64
libexec
libx32
local
sbin
share
src
Redirection of stderr (2> or 2>>)
To redirect a standard error, use 2> or 2>> after a command followed by a new standard error.

When you use 2>, the output will overwrite the existing contents while when you use 2>>, the output will be added at the end of the existing contents. To see how it works, run the command below as a normal user. As the normal user doesn't have the read permission to the /lost+found directory, you'll get an error message.
ls /lost+found
ls: cannot open directory '/lost+found': Permission denied
If you want to redirect the error message to the error.txt file, run the same command with redirection. By running the cat command, you can see that the error message is saved in the error file.
ls /lost+found 2> error.txt
cat error.txt
ls: cannot open directory '/lost+found': Permission denied
Redirection of stdout and stderr in the same file
If you want to record standard output and error in the same file, use >& symbol.

Redirection of stderr (2> or 2>>)
To redirect a standard error, use 2> or 2>> after a command followed by a new standard error.
When you use 2>, the output will overwrite the existing contents, while when you use >>, the output will be added at the end of the existing contents.
Redirection of stdin and stdout with the same command
You can redirect both standard input and output with the same command.

For example, to reverse the order of the content of the list.txt file and save it in the list_r.txt file, run the command below. By running the cat command, you can see that the item order has been reversed in the list_r.txt file.
sort -r < list.txt > list_r.txt
cat list_r.txt
src
share
sbin
local
libx32
libexec
lib64
lib32
lib
include
games
bin
Here is the summary of redirection symbols.






