chmod (Change Access Mode)

The chmod (CHange access MODe) command is used to change the access mode of files and directories.
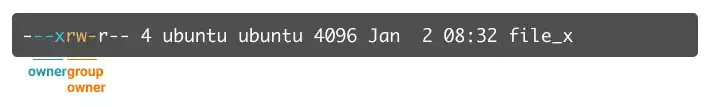
Three types of users and permissions
As was already explained in the beginning of this chapter, there are three types of users with different permissions. In this command, alphabets are assigned for each user type and all users.
u: owner userg: owner group userso: other usersa: all users
Also, there are three types of permissions.
r: Readw: Writex: Execute
Change operators
To change the access mode of each file or directory, you can combine a user type and a permission type with three types of symbols to set a change logic.
+: add permission-: remove permission=: overwrite permission
Here are some examples
g+w: addw(write) permission to group owner user (g)u-w: removew(write) permission from owner user (u)o=r: give onlyr(read) permission to other users (o)a=r: give onlyr(read) permission to all users (a)
Set permissions for multiple user types and permissions
You can set permissions for multiple user types at the same time by simply combining the characters like in the examples below
ug=rwx: give all permissions to owner user and owner group usersgo=r: give only read access to owner group users and other users
Set permissions for an entire directory recursively
To change permissions of an entire directory including sub-directory and files underneath, you can use the -R option.
For example, to change the permissions of the directory tree of dir_a1 in a way that grants read only permission to the group owner and other users, run the following command.
chmod -R go=r dir_a1
Check the owner group status of dir_a1 and dir_a2 by running the ls -l command. You can see that the group owner and other users have read only permission for both directories (dir_a1 and dir_a2). (Previously, the group owner and other users had execution permission for both directories. You can check their former statuses in the previous section.)
ls -l
drwxr--r-- 3 user_a user_a 4096 Jan 2 15:31 dir_a1
:
ls -l dir_a1
drwxr--r-- 2 user_a user_a 4096 Jan 2 15:31 dir_a2
 Note: Permission Conflict
Note: Permission Conflict
If the group owner's permission exceeds the owner user's permission, the group owner's permission will be restricted to the one set for the owner user. In the example below, as the owner doesn't have the read and write permission, the owner group user also cannot read and write although they have permission.