SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol)

SSH is used not only for remote login but also for file transfer in a secure way. There are two protocols to transfer files with SSH – SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) and SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol). In this section, we'll explain SFTP.
SFTP session and sub-commands
Unlike with SCP, after running the SFTP command, the SFTP session continues until you exit the session. Once the SFTP session is established, you can run sub-commands prepared for SFTP.
Establish SFTP session
There are two approaches to establishing an SFTP session – 1) without the SSH config file, and 2) with the SSH config file. The syntax is almost the same as the one of SSH. You can simply replace ssh with sftp.
Without the SSH config file, you need to specify the private key file path, user name, and IP address of the remote server.
sftp -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa ubuntu@54.169.91.239
With the SSH config file, the command is much simpler. Just type ssh and the SSH host name in your config file (the example below uses ssh_test as the SSH host name).
sftp ssh_test
Once the SFTP session is established, the command line changes to the one below.
SFTP sub-commands
During an SFTP session, you can run several SFTP sub-commands.
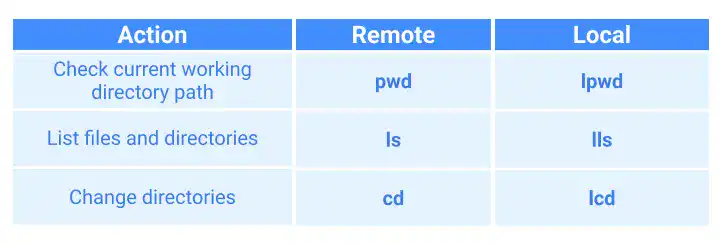
Check and change directories
SFTP provides sub-commands to check and change directories under both the remote server and the local computer. Here are the examples.
get command – download a file or directory from the remote server
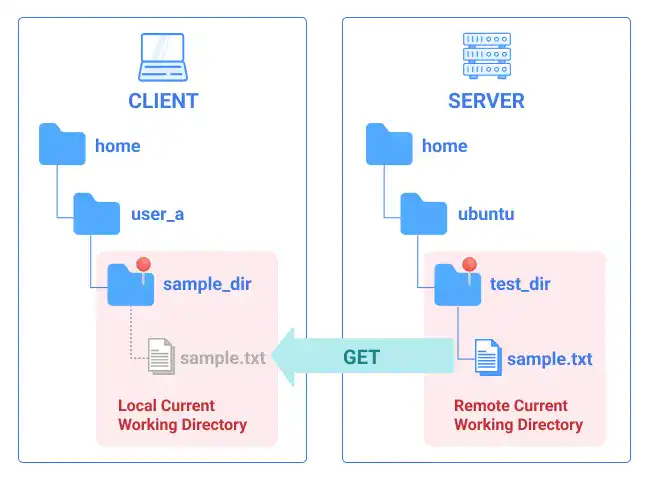
Once you set the current working directory on both the local computer and remote server, you can download the file from the remote server to the local computer with the get command.
For example, by running the command below, you'll transfer the sample.txt file under the current working directory on the remote server to the current working directory of your local computer.
get sample.txt
This is the illustration of the file transfer.
If you want to download a directory, use the -r option.
get -r sample_dir
put command – upload a file or directory to the remote server
To upload a file or directory from your local computer to the remote server, you can run the put command.
For example, by running the command below, you'll transfer the test.txt file under the current working directory on your local computer to the current working directory of the remote server.
put test.txt
exit (bye) command – stop the SFTP session
To end the session, run the exit (or bye) command.
exit
help command – check SFTP sub-commands
If you want to know more about SFTP sub-commands, the help command can be useful. It gives you a list of available SFTP sub-commands.
 Note: Difference between SCP and SFTP
Note: Difference between SCP and SFTP
One of the major differences between SCP and SFTP is while the SFTP protocol can resume data transfer which was stopped for some reason, SCP cannot resume it. To resume data transfer with SFTP, use the reget command.
For example, if you want to resume the sample_dir transfer, you can run the command below.
reget -r sample_dir





