Setting Up Linux Environment on AWS

Nowadays, Cloud Computing is very popular. Previously, to experience Linux OS, you needed to install Linux OS on your computer; however, it became easier to set up the Linux environment on public cloud infrastructure or VPS (Virtual Private Server). Throughout this course, we'll be using Linux Ubuntu OS on AWS Lightsail service to demonstrate Linux operations. AWS Lightsail is a VPS. AWS Lightsail is a light version of AWS EC2. Without detailed configuration, you can set up the Linux OS environment very quickly. As AWS Lightsail offers the first three months free, you can use Linux OS at no additional cost.
Here are the key steps to set up the Linux OS environment on AWS Lightsail.
Set up an AWS account
If you don't have an AWS account, create it first. It takes only a few minutes.
Go to the AWS website (https://aws.amazon.com/).
Click on the orange Sign In to the Console button.

Fill in the following information and verify your email address
- Root user email address
- AWS account name
By following the remaining instructions, you can create an AWS account.
The remaining steps are listed below.
- Create your password
- Add your contact information
- Add a payment method
- Verify your phone number
- Choose an AWS Support plan
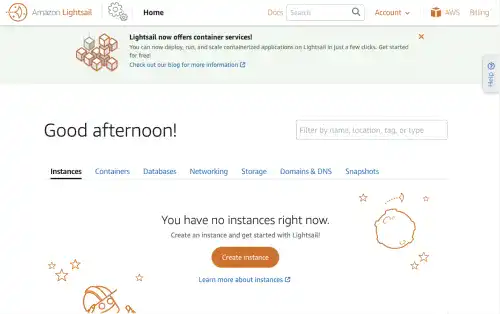
Start using Lightsail
When you log in to your AWS account, you start at AWS Console Home.
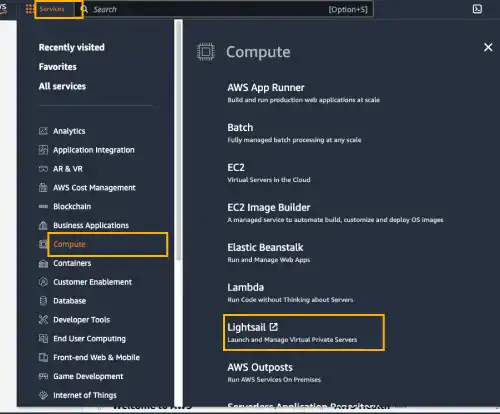
Select Services on the top left and click on Compute. You can find Lightsail in the menu. Click on Lightsail to go to Lightsail Home.
On Lightsail Home, press the Create Instance button.
Select Linux/Unix as a platform and select Ubuntu (20.04 LTS) under the OS only selection.
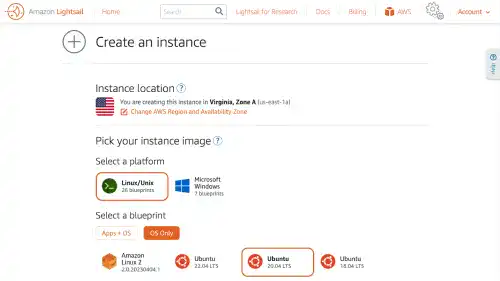
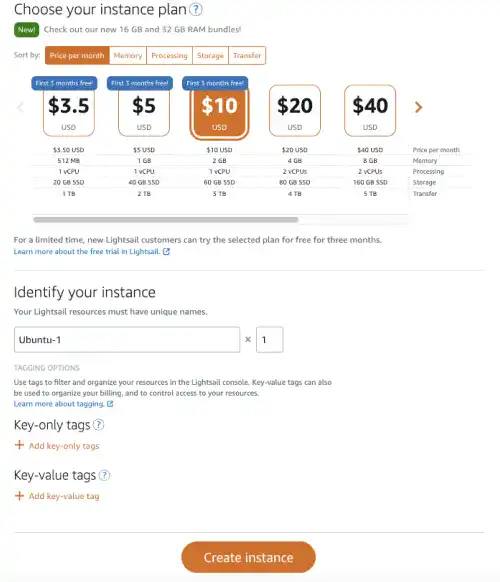
Scroll down to choose an instance plan. Select one of the free plans. Here we select the $10 plan. Higher price plans provide better virtual machine specs. To create an instance, click on the Create instance button at the bottom.
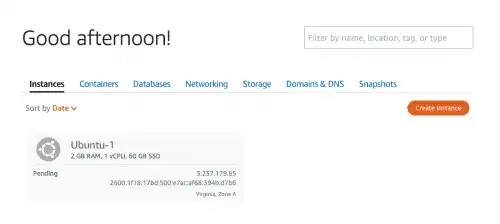
After pressing the Create instance button, you'll see that Ubuntu OS is being prepared. While the icon is gray, instance creation is still pending.
Once the instance is launched, you can see that icons change color. Click the Ubuntu OS panel to see the details of the OS.
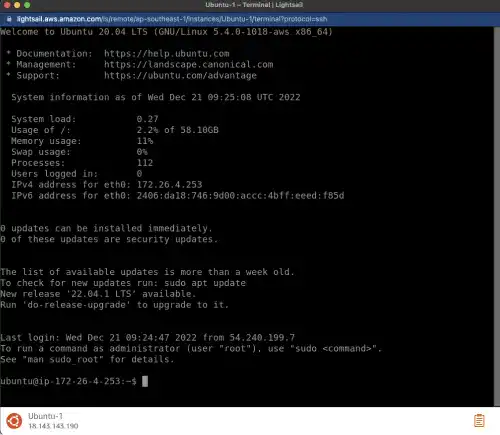
Under the Connect menu, you can access Ubuntu Linux OS through your web browser. Click on the orange Connect Using SSH button to launch the browser-based command line.
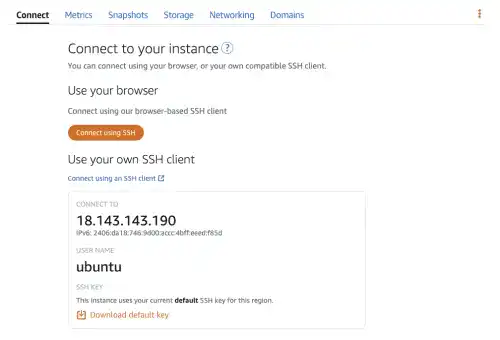
You can also directly open the command line from the Instance panel. Click on the orange command line icon to launch the command line.
The command line will show up in a new window as shown in the image below. Now you are ready to use Linux OS.