GitHub SSH Setup

To establish an SSH connection, you need an SSH key pair (a private key and a public key) and upload the public key to the GitHub platform.
One of the benefits of SSH connection is the easiness of connecting to the GitHub repository. If you skip setting a passphrase or use ssh-agent, you don't need to type a passphrase every time you connect with a GitHub repository.
There are several approaches in SSH settings. In this topic, we'll explain the most simple one. In the next topic, we'll explain more advanced settings using ssh-agent and customizing the SSH key file path. If you want to pursue the advanced settings, you can skip this page and go to the next page.
In the approach that we'll explain on this page, there are four key steps:
- Generate an SSH key pair
- Copy the public key
- Upload the public key to GitHub
- Test connection with GitHub
Generate an SSH key pair
The first step in SSH setup is to generate a new SSH key pair. To generate it, run the command below.
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "your email address"
File path
When running the command, you’ll be asked to enter the file in which to save the key. You can specify a file path or you can just hit the enter key to skip. If you skip the setting, the key pair will be created in the default path.
Passphrase
When running the command, you’ll be asked to set a passphrase. This passphrase gives another layer of security. If you don't want to type a passphrase every time you connect to GitHub, you can skip setting a passphrase although the security level decreases.
To set a passphrase, type your passphrase twice. Save the passphrase as the passphrase is used when you establish ssh connection.
When the command is executed, the files of the public and private keys are generated under the .ssh directory under your user home directory. As it is a hidden directory, you need to change the settings to show the hidden directory. For Mac OS, press the shift + command + . keys.
Command Options
-t option is to set security type. rsa has mainly been used; however, GitHub recommends ed25519 now for better security. If you are using a legacy system that doesn't support the Ed25519 algorithm, you can use rsa. The command to generate an SSH key is the one below.
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C “your email address”
Check this link GitHub – Generating a new SSH key for more details.
-C option is to overwrite a comment in the key. As the default comment is username@hostname, it is good to overwrite to avoid disclosing your hostname. Typically, an email address is used for the comment.
Copy the public key
To add the public key to GitHub in the next step, you need to copy it first.
cat command
Show public key content by running the cat command.
cat file_path
Copy the displayed public key and go to the next step.
pbcopy or clip command
Alternatively, you can directly copy the content of the file without displaying the file content by using the pbcopy command for Mac,
pbcopy < file_path
or the clip command for Windows.
clip < file_path
For Linux, a similar command may not be available by default unless you install it.
Upload the public key to GitHub
You need to add the copied public key to the GitHub account setting page by conducting the following actions.
- Go to the GitHub website
- Click your icon
- Press the Settings button
- Select SSH and GPG keys on the left side bar
- Press New SSH key button
- Set Title and paste the public key
Test connection with GitHub
You can check if you can connect with GitHub using the ssh command with the -T option.
ssh -T git@github.com
You'll see a message confirming that you’ve been successfully authenticated.
Practice
Objective:
Set up an SSH connection to GitHub
In this practice example, we use bloovee as a username and bloovee@example.com as an email address. You need to change them to your own username and email.
Note: The file path shown in the command line response is an example based on Mac OS.
1. Generate an SSH key pair
Run the ssh-keygen command
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "bloovee@example.com"
After running the command, you’ll be asked to indicate the file path to save the file.
Generating public/private ed25519 key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/Users/bloovee/.ssh/id_ed25519):
The default SSH key path
The default SSH key file paths are slightly different by OS as the OS user home directory paths are different.
Windows: /C/Users/bloovee/.ssh/id_ed25519
Linux: /home/bloovee/.ssh/id_ed25519
To create an SSH key pair in the default file path, hit the enter key. You'll be asked for a passphrase.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
To create the key pair without a passphrase, hit the enter key two times. A key pair is saved under the file path displayed. You'll see the following response in your command line.
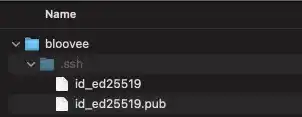
Your identification has been saved in /Users/bloovee/.ssh/id_ed25519
Your public key has been saved in /Users/bloovee/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:xxxxxxxxxxxxxx bloovee@example.com
The key's randomart image is:
+--[ED25519 256]--+
| ..E |
| o |
| o + .. . |
| & = +. . o|
| + X.S.. =.|
:
+----[SHA256]-----+
You can confirm that the two files are generated in the .ssh directory under your home directory. The .ssh directory is a hidden directory. If you cannot see it, you need to make hidden directories and files visible. For Mac, press the shift + command + . keys.
2. Copy the public key
cat command
Show public key content by running the cat command.
cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
ssh-ed25519 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx bloovee@example.com
Copy the displayed public key and go to the next step.
pbcopy or clip command
Alternatively, you can directly copy the content of the file without displaying it by using the pbcopy command for Mac, or the clip command for Mac
For Mac:
pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
For Windows:
clip < ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
3. Upload the public key to GitHub
Go to the GitHub website, click your icon, and press the Settings button.
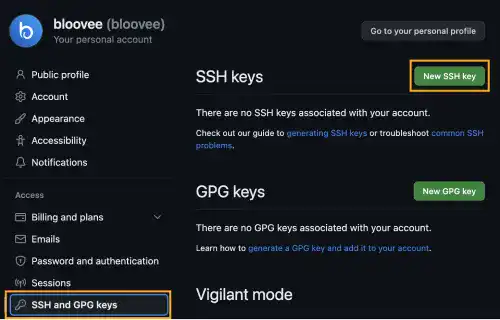
Select the SSH and GPG keys on the left sidebar and press the New SSH key button.
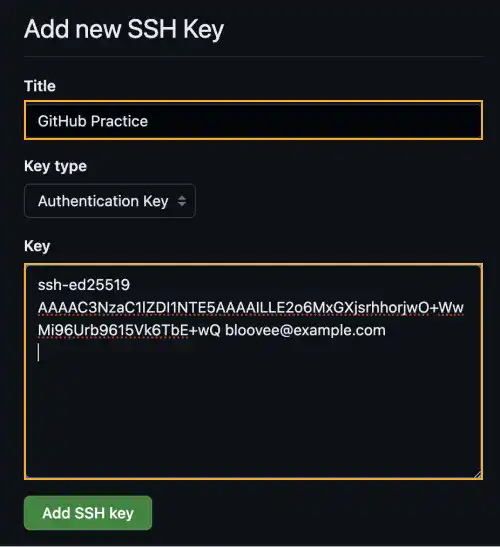
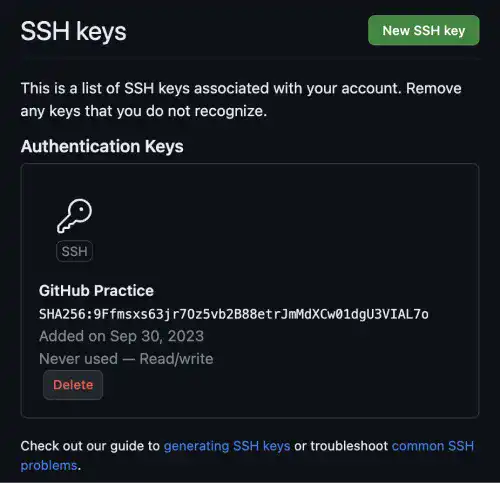
Fill title name (any name) in the Title field and paste the public key information in the Key field.
You'll see that the public key is registered.
4. Test connection with GitHub
Run the ssh command with the GitHub URL.
ssh -T git@github.com
You may get the following message if you are connecting to GitHub first time.
The authenticity of host 'github.com (20.27.177.113)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:+DiY3wvvV6TuJJhbpZisF/zLDA0zPMSvHdkr4UvCOqU.
This key is not known by any other names
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])?
Type yes and hit the enter key
If the test connection is successful, you'll see the message below.
Hi bloovee! You've successfully authenticated, but GitHub does not provide shell access.
Now, you are ready to connect to GitHub with SSH.





