Check Status of Working Tree and Staging Area – git status

git status is the command that can be used to see the status of the Working Tree and the INDEX. This status lets you see which changes have been staged, which haven't, and which files aren't tracked by Git.
There are two types of information that the git status command provides: branch status and commit status. On this page, we'll mainly cover the second one (commit status).
1. Branch status: on which branch you are currently working (the branch concept will be explained in the next chapter)
2. Commit status mainly covers the following status
- Existence of untracked files
- Existence of not staged files
- Files in INDEX (Staging Area) but not committed yet
- All files are tracked and committed
Here are detailed explanations with examples of typical git status responses.
1. Existence of untracked files
When you haven't run a commit before and haven't staged any files, the files can have the statuses shown in the illustration below.
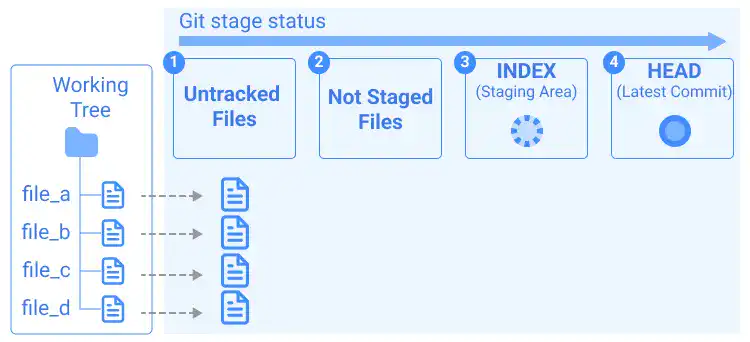
When you run the git status command, you'll see a message like below.
On branch master
No commits yet
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
file_a
file_b
file_c
file_d
2. Existence of not staged files
In typical git operations, you'll add the files to INDEX...
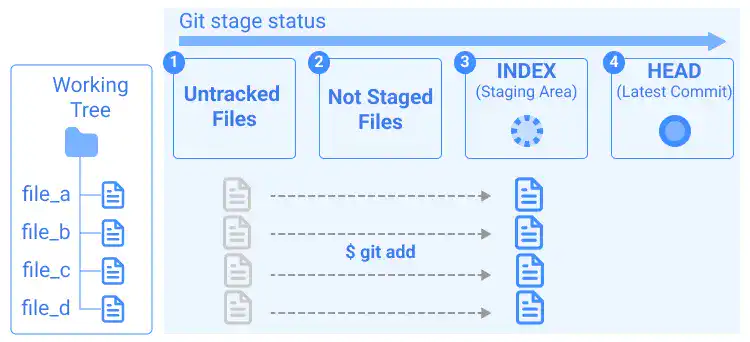
...and commit the files.
After everything is committed, you may edit some files like in the illustration below. The files are already tracked in the operations above but changes are not staged yet.
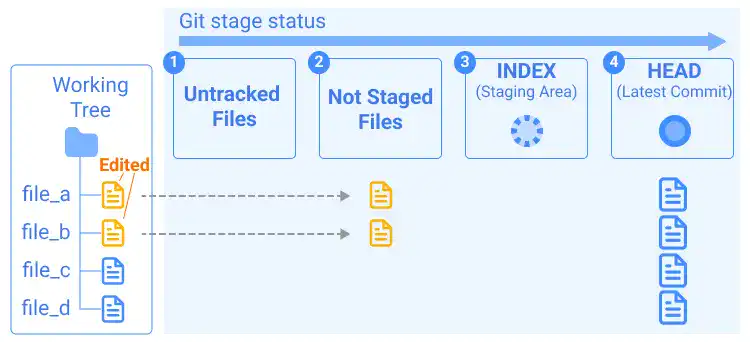
When you run the git status command under this situation (before you add the changes to INDEX), you'll see a message like below.
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: file_a
modified: file_b
3. Files in the INDEX (Staging Area) but not committed yet
If you staged the modified files by the git add command but have not committed them yet, the files can have the statuses shown in the illustration below.
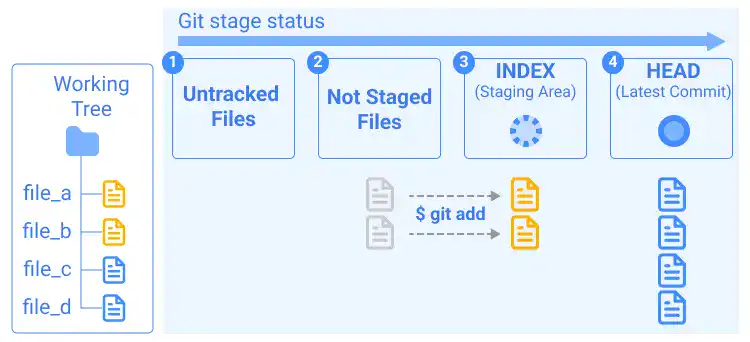
When you run the git status command in this situation (before you commit the changes), you'll see a message like below.
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: file_a
modified: file_b
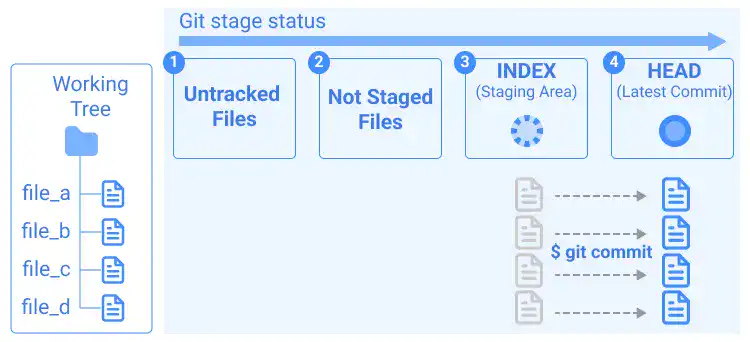
4. All files are tracked and committed
After you commit all the changes like in the illustration below...
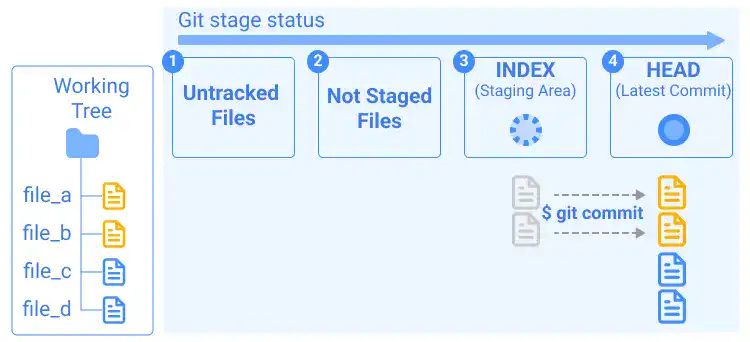
..., you'll see a message like below.
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean





