What Are Website Performance and Page Experience?

Page Experience refers to a set of signals that Google uses to measure how users perceive the experience of interacting with a web page beyond its pure information value.
Google Search Central, the Google official document, describes page experience in four aspects: Core Web Vitals, Mobile Friendliness, Security, and Intrusive Interstitials and Dialogs.
Core Web Vitals
As explained earlier in Technical SEO Audit, Google introduced Core Web Vitals as a set of specific factors to determine a webpage's overall user experience from the speed and UI stability point of view. Core Web Vitals include:
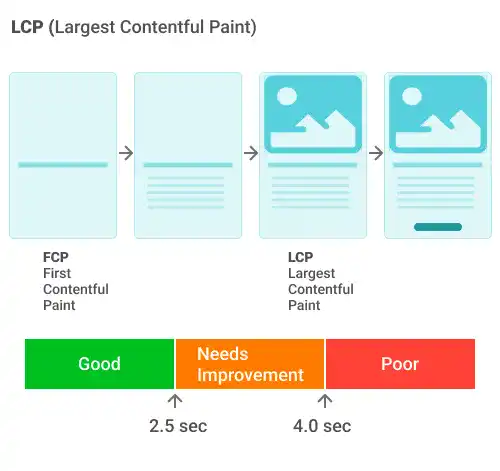
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP):
- LCP measures loading performance, the time it takes for the largest content element visible in the viewport to load and render fully on the page.
- This could be an image, video, or a block of text. LCP is important for understanding user experience, as it indicates how long a user waits to see the main content of a page.
- A good LCP score is 2.5 seconds or faster.
For more details, refer to this article by web.dev – Largest Contentful Paint (LCP).
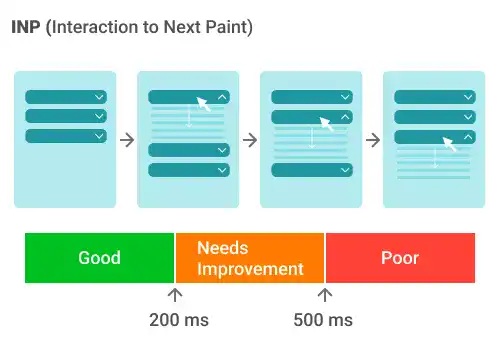
Interaction to Next Paint (INP):
- INP is a newly developed metric that replaced First Input Delay (FID) as one of the Core Web Vitals on March 12, 2024.
- INP measures interactivity, the responsiveness of a web page, by quantifying the delay between user interactions (such as clicks, taps, or key presses) and the visual response or feedback from the page.
- Unlike metrics focusing solely on load performance, INP captures the user's experience of a site's interactivity and responsiveness throughout their visit.
- It aims to identify the worst-case latency of critical user interactions, providing insights into the site's perceived speed and fluidity.
- A good INP score is 200 milliseconds or faster.
For more details, refer to this article by web.dev – Interaction to Next Paint (INP).
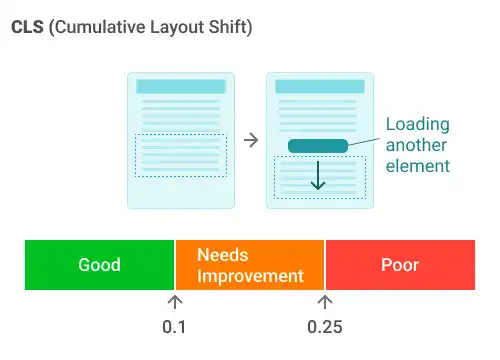
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS):
- CLS measures a website's visual stability by quantifying how much content shifts on the screen during the loading phase.
- These shifts can occur when elements on the page load asynchronously or when elements are dynamically added to the page, causing unexpected movement of content that the user was viewing or interacting with.
- A good CLS score is 0.1 or less.
For more details, refer to this article by web.dev – Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
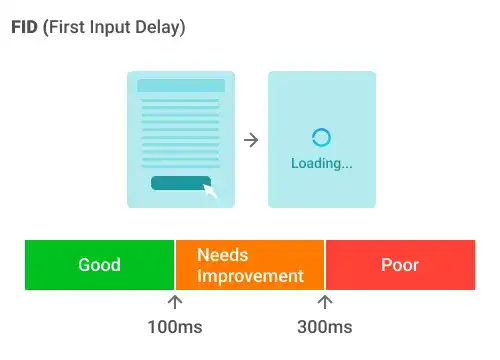
Note: First Input Delay (FID):
- First Input Delay (FID) measures interactivity. It was one of the Core Web Vitals until it was replaced by Interaction to Next Paint (INP).
- FID measures the time from when a user first interacts with a page (i.e., when they click on a link, tap on a button, etc.) to when the browser can actually begin processing event handlers in response to that interaction.
- A good FID score is 100 milliseconds or faster.
- First Input Delay (FID) only accounts for the first interaction, while INP covers all page interactions. FID also only measures the first interaction's input delay. It doesn't have time to run event handlers or the delay in presenting the next frame.
For more details, refer to this article by web.dev – First Input Delay (FID).
Mobile-Friendliness
Mobile-friendliness includes responsive design (where the site layout adjusts to fit the screen size), fast loading times, accessible menus and buttons, and readable text without zooming.
Creating a mobile-friendly site is essential as Google emphasizes mobile-first indexing – Google predominantly uses the mobile version of a site's content, crawled with the smartphone agent, for indexing and ranking.
Responsive design is one of the most critical techniques for building a mobile-friendly website. It adjusts the website design to any screen size, ensuring optimal viewing across devices. It uses flexible layouts and CSS media queries to adapt to the user's device, improving accessibility and user experience. This approach eliminates the need for device-specific designs, making websites universally usable.
For more details, refer to this Google Search Central documentation – Mobile site and mobile-first indexing best practices.
Security
Security directly affects user trust and safety when visiting a website. Search engines prioritize secure websites in their rankings to provide users with safe browsing experiences.
HTTPS
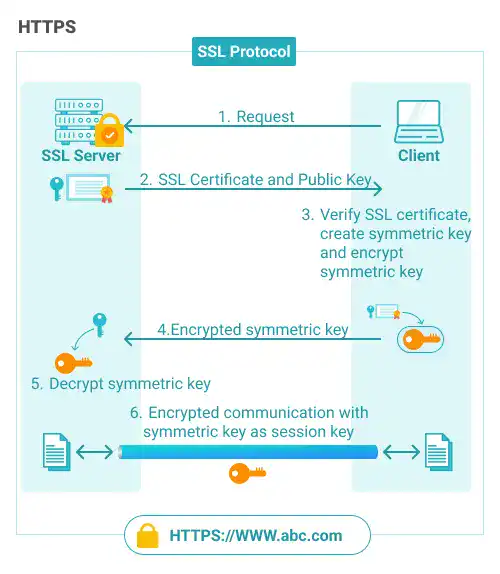
Websites secured with HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypt data transmitted between the user and the server, protecting against eavesdropping, tampering, and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Google has confirmed HTTPS as a ranking signal, meaning secure websites may rank higher than their non-secure counterparts.
To use HTTPS, you need to set up SSL (Secure Sockets Layers). To understand how to set up SSL, you can refer to our SSL Setup guide.
Safe Browsing
Websites should be free from malware, phishing, and deceptive content. Search engines penalize sites that may potentially compromise user safety by removing them from search results or marking them as unsafe.
Intrusive Interstitials and Dialogs
Intrusive interstitials and dialogs refer to pop-ups, overlays, and modal dialogs that significantly hinder or obstruct the view of the main content on a webpage.
With limited screen space, these elements can be particularly disruptive on mobile devices.
They include advertisements, subscription forms, and prompts that cover the content or require user action to be dismissed.
Google and other search engines may penalize websites using intrusive interstitials, especially if they appear before accessing the main content, as they negatively impact the user experience and accessibility of the website.
For more details, refer to this Google Search Central documentation – Avoid intrusive interstitials and dialogs.





