Search Engines and Ranking Algorithms: Decoding the Mechanics

Before learning SEO, it is imperative to establish a comprehensive understanding of Search Engines.
Users experience a straightforward process of entering queries and receiving results on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP), which includes organic results, paid ads, and rich results.
Behind this user's simplicity, search engines perform intricate functions. Crawling involves collecting data from web pages, which is then parsed and stored (indexing). The ranking algorithm evaluates indexed pages based on various factors to determine search rankings.
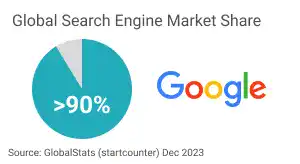
Google's Search Engine Market Share
According to GlobalStats, Google maintains more than 90% of the search engine market share globally. Based on this fact, you must first understand Google's search engine.
Other search engines besides Google include Bing by Microsoft, Yahoo, Baidu, and Yandex. The core principles of SEO can also be applied across various search engines, although each has unique characteristics in its algorithm, crawling and indexing approaches, and user demographics.
The Latest Trends
While Google still holds over 90% of the global search engine market share, user behavior is evolving beyond traditional web searches. Social media platforms like TikTok and Instagram are increasingly used for discovery, particularly among Gen Z, who favor short-form videos and influencer-driven recommendations. AI-powered answer engines, such as ChatGPT and Perplexity AI, are also gaining traction by providing direct, conversational responses without requiring users to browse multiple web pages. Additionally, vertical search engines specializing in areas like travel, healthcare, and e-commerce are growing in importance, offering tailored results for specific industries. These trends indicate that search behavior is diversifying, with users leveraging multiple platforms to find information more efficiently.
Despite these shifts, traditional search engines remain a critical component of online visibility. Google’s integration of AI-generated overviews into its search results reflects its ongoing relevance, as the majority of online searches still begin on Google. While alternative search methods are expanding, they often complement rather than replace traditional search. Businesses and content creators must continue SEO for traditional search engines to maintain strong visibility and organic traffic. Optimizing for Google and Bing ensures content remains discoverable across various search touchpoints, including AI-powered summaries, featured snippets, and voice search. As search evolves, adapting SEO strategies to both traditional and emerging search platforms will be essential for maximizing online reach and engagement.
In this chapter, we’ll cover the following SEO foundational topics:
- How Do Search Engines Work?
- Search Ranking Results - Ranking Algorithms
- The Google 200 Ranking Factors Myth
Learn offline for better focus!
A book for this course is available on Amazon.
SEO Tutorial for Beginners
Master the Essentials of Search Engine Optimization
Get the Book Now



