Pseudo Elements in CSS

CSS pseudo elements offer a unique way to style specific parts of an element without directly altering the HTML structure. They allow you to control the appearance of content like the first letter of a paragraph, or even add content before or after elements, enhancing web design flexibility. This guide will introduce you to the concept of pseudo elements in CSS, their various use cases, and how to leverage AI tools to generate CSS code efficiently. By mastering pseudo elements, you can significantly enhance your web design capabilities while maintaining clean and maintainable code.
In this section, we’ll cover the following topics:
- What Are Pseudo Elements in CSS?
- Utilizing Pseudo Elements with AI
What Are Pseudo Elements in CSS?
CSS pseudo elements are keywords added to a selector that enable you to style certain parts of an element. Unlike traditional CSS selectors, which style an entire element, pseudo elements target specific sub-parts of elements, such as text content, and allow you to add decorative or functional content around them without modifying the underlying HTML.
Commonly Used Pseudo Elements in CSS
Here are some of the most commonly used pseudo elements in CSS:
::before: Adds content before an element.::after: Adds content after an element.::first-letter: Styles the first letter of a block of text.::first-line: Styles the first line of a block of text.::selection: Styles the portion of text that is highlighted by the user.::marker: Targets the marker of a list item (<li>) in ordered or unordered lists, allowing you to style bullets or numbering.::placeholder: Styles placeholder text within input fields (<input>, <textarea>), commonly used to change the color or style of placeholder text.
Example: Styling with ::before and ::after
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Pseudo Elements Example</title>
<style>
.highlight::before {
content: "Start: ";
color: red;
}
.highlight::after {
content: " End.";
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="highlight">This is an example sentence.</p>
</body>
</html>
In this example, the ::before pseudo element adds the word “Start:” before the text, while ::after adds “End.” after the text. Both are styled without needing to modify the HTML structure, showcasing the power of pseudo elements.
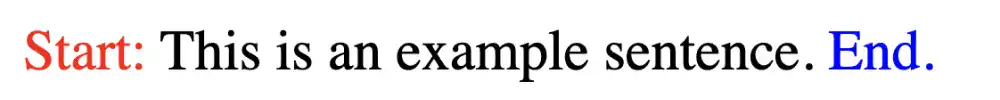
How Pseudo Elements Improve Web Design
Pseudo elements are a highly effective way to enhance your web design by allowing precise styling control. For example, you can use them to improve typography, add decorative elements, or inject custom content without bloating your HTML. This approach helps keep your HTML cleaner and more maintainable while providing the flexibility to implement creative styles.
Differences Between Pseudo Elements and Pseudo Classes
Pseudo elements and pseudo classes are often confused, but they serve different purposes. While pseudo elements target specific parts of an element (e.g., first letter or line), pseudo classes apply styles based on an element’s state (e.g., :hover, :focus). Understanding when to use each can improve the efficiency of your CSS and enhance the user experience.
Utilizing Pseudo Elements with AI
AI tools can significantly streamline your CSS development process by generating code based on descriptions or prompts. In this section, we will explore how to use AI to create pseudo element styles efficiently. By leveraging AI, you can save time and focus on fine-tuning your design rather than writing repetitive CSS.
Preparing for Practice Files
This course takes a hands-on approach, allowing you to apply the techniques covered in real-world scenarios. We'll be using a structured folder layout. Before proceeding with the examples, please ensure the following files are prepared:
/your-project-folder/
├── 04-03-pseudo-elements-in-css/ (<- sub-folder)
├── example-1.css
├── example-1.html
├── example-2.css
├── example-2.html
├── example-3.css
├── example-3.html
├── example-4.css
├── example-4.html
├── example-5.css
├── example-5.html
├── example-6.css
├── example-6.html
├── example-7.css
├── example-7.html
For your convenience, these files are also available on our GitHub repository. You can download the practice files to follow along with the case studies presented in this guide.
AI Case 1: Styling Elements with ::before
In this example, we will use an AI-generated prompt to create CSS code that adds custom content before a paragraph using the ::before pseudo element.
Sample AI prompt:
Generate CSS code that adds custom content before a paragraph element using the ::before pseudo element.
Sample code output:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Pseudo Elements Example 1</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="example-1.css" />
</head>
<body>
<p class="highlight">Hello World!</p>
</body>
</html>
.highlight::before {
content: "Intro: ";
font-weight: bold;
color: green;
}
Instructions to see the results:
- Save the code above in
example-1.htmlandexample-1.cssin the04-03-pseudo-elements-in-cssfolder. - Open
example-1.htmlin your browser to view the text “Intro: Hello World!” where “Intro:” is styled in green.
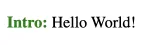
Visit this link to see how it looks in your web browser.
AI Case 2: Styling Elements with ::after
In this case, we’ll add content after a paragraph element using the ::after pseudo element.
Sample AI prompt:
Generate CSS code that adds custom content after a paragraph element using the ::after pseudo element.
Sample code output:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Pseudo Elements Example 2</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="example-2.css" />
</head>
<body>
<p class="highlight">Hello World!</p>
</body>
</html>
.highlight::after {
content: " Goodbye!";
font-style: italic;
color: blue;
}
Instructions to see the results:
- Save the code above in
example-2.htmlandexample-2.css. - Open
example-2.htmlin your browser to view “Hello World!” followed by “Goodbye!” styled in blue italics.

Visit this link to see how it looks in your web browser.
AI Case 3: Creating Decorative Content with ::before and ::after
In this example, we will use both the ::before and ::after pseudo elements to add decorative content around an element.
Sample AI prompt:
Generate CSS code that adds a decorative element before and after a paragraph using the ::before and ::after pseudo elements.
Sample code output:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Pseudo Elements Example 3</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="example-3.css" />
</head>
<body>
<p class="highlight">
This paragraph is framed by decorative elements using ::before and
::after.
</p>
</body>
</html>
.highlight::before {
content: ">>> ";
color: green;
font-weight: bold;
}
.highlight::after {
content: " <<<";
color: blue;
font-weight: bold;
}
Instructions to see the results:
- Save the code above in
example-3.htmlandexample-3.cssin the04-03-pseudo-elements-in-cssfolder. - Open
example-3.htmlin your browser to see the decorative content added before and after the paragraph.
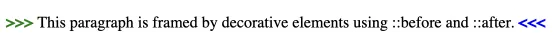
Visit this link to see how it looks in your web browser.
AI Case 4: Styling Text with ::first-letter and ::first-line
In this example, we will style the first letter and the first line of a paragraph using pseudo elements.
Sample AI prompt:
Generate CSS code that styles the first letter of a paragraph element in bold and the first line of the paragraph in italics.
Sample code output:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Pseudo Elements Example 4</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="example-4.css" />
</head>
<body>
<p class="highlight">
This is the first line of the example sentences for demonstrating the
::first-letter and ::first-line pseudo elements in CSS.<br />
This is the second line of the example sentences for demonstrating the
::first-letter and ::first-line pseudo elements in CSS.
</p>
</body>
</html>
.highlight::first-letter {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
}
.highlight::first-line {
font-style: italic;
}
Instructions to see the results:
- Save the code above in
example-4.htmlandexample-4.cssin the04-03-pseudo-elements-in-cssfolder. - Open
example-4.htmlin your browser to view the first letter styled in bold and the first line of the paragraph in italics.

Visit this link to see how it looks in your web browser.
AI Case 5: Using Pseudo Elements for Hover Effects
In this final example, we will use the ::before pseudo element in combination with the :hover pseudo class to create hover effects.
Sample AI prompt:
Generate CSS code that displays a decorative element before a paragraph when the user hovers over it using the ::before pseudo element and the :hover pseudo class.
Sample code output:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Pseudo Elements Example 5</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="example-5.css" />
</head>
<body>
<p class="highlight">Hover over this text to see the hover effect.</p>
</body>
</html>
.highlight:hover::before {
content: "Hovered: ";
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
Instructions to see the results:
- Save the code above in
example-5.htmlandexample-5.cssin the04-03-pseudo-elements-in-cssfolder. - Open
example-5.htmlin your browser and hover over the text to see the decorative content appear before the paragraph.
Watch this video to see what it looks like.
Visit this link to see how it looks in your web browser.
AI Case 6: Styling List Markers with ::marker
In this example, we will style the list markers of an unordered list using the ::marker pseudo element. This pseudo element lets us customize the color, font, and other stylistic properties of list markers, giving more control over the appearance of bullet points.
Sample AI prompt:
Generate CSS code to change the color and size of list markers in an unordered list using the ::marker pseudo element.
Sample code output:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Pseudo Elements Example 6</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="example-6.css" />
</head>
<body>
<ul class="custom-list">
<li>First item</li>
<li>Second item</li>
<li>Third item</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
.custom-list li::marker {
color: teal;
font-size: 1.5em;
font-weight: bold;
}
Instructions to see the results:
- Save the code above in
example-6.htmlandexample-6.cssin the04-03-pseudo-elements-in-cssfolder. - Open
example-6.htmlin your browser to see the customized list markers. The list bullets should appear in teal color, larger in size, and bolded.

Visit this link to see how it looks in your web browser.
AI Case 7: Custom List Markers with ::before
In this example, we’ll use the ::before pseudo element to create custom markers for list items, replacing the default bullets with icons or text symbols.
Sample AI prompt:
Generate CSS code to replace default list markers with gradient-colored circles using the ::before pseudo-element.
Sample code output:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Pseudo Elements Example - Gradient Circle Markers</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="example-7.css" />
</head>
<body>
<ul class="gradient-marker-list">
<li>Define your project scope</li>
<li>Create a detailed timeline</li>
<li>Allocate resources effectively</li>
<li>Monitor progress continuously</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
/* Remove default list style */
.gradient-marker-list {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.gradient-marker-list li {
position: relative;
padding-left: 2em; /* Space for custom marker */
margin-bottom: 0.8em;
font-size: 1.1em;
display: flex;
align-items: center; /* Align items vertically */
}
/* Custom gradient circle marker */
.gradient-marker-list li::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
left: 0;
width: 0.8em;
height: 0.8em;
border-radius: 50%; /* Make the marker circular */
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #ff6ec4, #7873f5);
translate: 10px;
}
Instructions to see the results:
- Save the code above in
example-7.htmlandexample-7.cssin the04-03-pseudo-elements-in-cssfolder. - Open
example-7.htmlin your browser to see the customized list markers.

Visit this link to see how it looks in your web browser.
Best Practices for Using Pseudo Elements in CSS
CSS pseudo elements provide powerful ways to style specific parts of an element without changing the HTML structure. Here are some best practices to follow for effective use of pseudo elements in your CSS:
- Select the Right Pseudo Element: Use
::beforeand::afterfor adding decorative or content-related elements before or after text blocks. For text styling, rely on::first-letterand::first-lineto enhance typography without altering the HTML. - Keep HTML Clean: By using pseudo elements, you avoid adding extra HTML tags solely for styling purposes, which keeps your code more readable and maintainable.
- Use Consistent Content: Ensure the content added through
::beforeor::afteris consistent across pages to maintain design coherence, especially when used for branding or decoration. - Optimize for Performance: Limit excessive pseudo elements on a single page, as each additional style requires more rendering power. This helps keep page loading times low.
Following these practices will help you achieve cleaner HTML and more creative, maintainable CSS. With pseudo elements, you can bring a unique flair to your web design efficiently and effectively.




