Masking and Boolean Operations in Figma

Masking and Boolean operations are powerful tools in Figma that allow you to create complex designs by combining or subtracting shapes, and by selectively revealing parts of your design. Whether you’re looking to craft intricate patterns, merge elements, or create cutouts, mastering these techniques will greatly expand your design capabilities and streamline your workflow. In this guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of masking and Boolean operations, providing you with practical tips and examples to enhance your Figma projects.
In this section, we’ll cover the following topics.
- Masking
- Boolean Operations
Masking
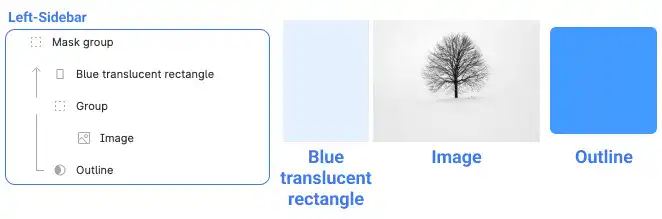
Masking in Figma is a powerful feature that allows you to control the visibility of objects by using a specific shape to “mask” or hide parts of other layers. This is especially useful when you want to reveal only a portion of an image or complex design.
Basic Masking Technique:
In Figma, you can fill a shape with an image, but when dealing with multi-layered objects, masking becomes essential. Masking enables you to trim and control the visibility of objects using a specific shape. The shape you select acts as a mask, and any objects placed above it in the layer hierarchy are trimmed according to the mask’s boundaries.
Example: If you have an image and want to display it within a circular shape, you can place the circle above the image and use it as a mask. The result is that only the portion of the image within the circle is visible, while the rest is hidden. Watch the video below.
Editing Masked Objects:
Even after applying a mask, each element remains editable within its layer. This means you can modify individual components, such as changing the image within the mask, without affecting the overall structure of the design. This flexibility allows for non-destructive editing, which is crucial in maintaining the integrity of your design while making adjustments.
Boolean Operations
Boolean operations are useful to create custom shapes. There are four Boolean operations in Figma.
Types of Boolean Operations
There are four main Boolean Operations.
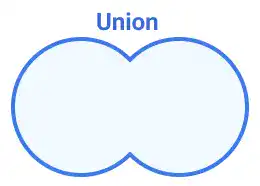
Union:
Combines two or more shapes into a single shape, merging their areas into one unified object.
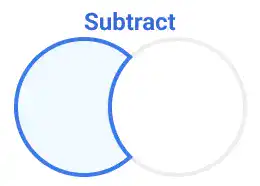
Subtract:
Removes the area of one shape from another. The shape in the top layer subtracts from the shape beneath it.
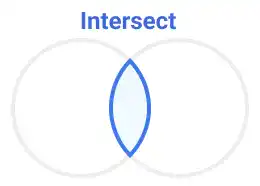
Intersect:
Displays only the overlapping area of selected shapes, hiding everything else.
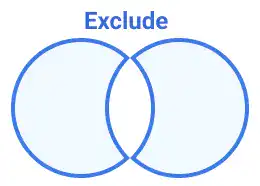
Exclude:
Hides the overlapping area of selected shapes, showing only the non-overlapping parts.
Perform Boolean Operations
Executing a Boolean operation in Figma is straightforward:
- Select the Objects: Choose the shapes you want to manipulate.
- Access Boolean Operations: Click on the two-square icon located in the top center of the canvas.

- Choose an Operation: Select from Union, Subtract, Intersect, or Exclude to apply the desired effect.
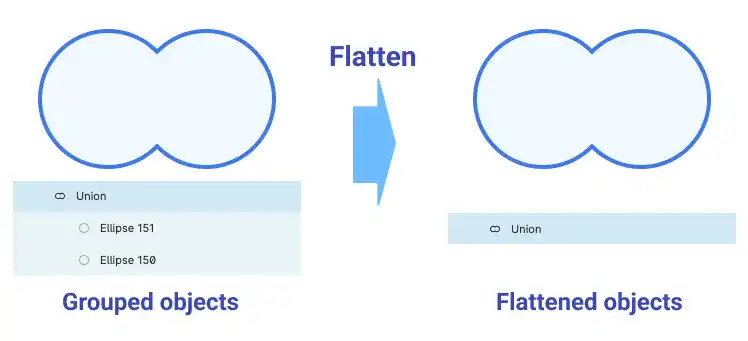
Flatten Boolean Groups
Each object that a Boolean operation was executed for still remains under an object group (union, subtract, intersect or exclude). If you want to make the object group one object, you need to flatten the group. You can flatten objects from the right-click menu.
The flattened object will become one vector object. You cannot edit original elements anymore; however, the flattened object is more stable when you change the size of the object. (Grouped objects might not be properly scaled.)