Understanding Constraints in Figma for Responsive Design

Constraints in Figma are essential for creating designs that adapt smoothly to various screen sizes and layouts. By setting constraints on your design elements, you ensure they maintain their position and proportion when the frame is resized. This article will guide you through the basics of using constraints in Figma, helping you build responsive, flexible designs that look great on any device.
In this section, we’ll cover the following topics.
- What is Constraint?
- How to set constraints?
What is Constraint?
A constraint in Figma is a powerful tool that controls the positioning and scaling of objects within a frame. It ensures that design elements remain aligned and proportional, regardless of changes to the frame size. For instance, when designing a navigation bar, you may want the brand logo to stay centered while the menu icon remains on the left and the search icon and avatar stay on the right. Constraints allow you to achieve this easily, ensuring a consistent layout across different screen sizes.
Example:
In a navigation bar, you might apply a vertical center constraint to all elements, ensuring they remain centered vertically, while setting specific horizontal constraints:
• Hamburger menu: Left constraint
• Brand logo: Center constraint
• Avatar and search icon: Right constraint
This setup ensures that as the navigation bar resizes, the elements maintain their intended positions, creating a responsive and cohesive design. Watch the video below.
How to set constraints?
Setting constraints in Figma is straightforward. Follow these steps:
- Select the Object: Click on the design element you want to set constraints for.
- Access Constraints Section: In the right sidebar, you’ll find the constraints section. This panel allows you to choose how your object should behave when the frame is resized.
In the constraints panel, you can specify which edges of the frame the object should be fixed to, and how it should resize. For example, you can:
- Pin an object to the top-left corner, ensuring it stays in that position even if the frame grows or shrinks.
- Center an object both horizontally and vertically, keeping it in the middle regardless of frame changes.
- Allow an object to scale with the frame, maintaining its relative size and position.
Watch the video below.
Practical Examples of Constraints
To understand how constraints work in different scenarios, consider the following examples:
- Top Left Constraint: This setting keeps an object anchored to the top left of the frame, ensuring it remains in the same position relative to the top-left corner as the frame resizes.
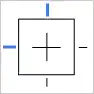
Watch the video below.
- Bottom Right Constraint: This anchors the object to the bottom right of the frame, ideal for elements like buttons or logos that need to stay in the bottom right corner.
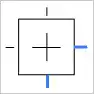
Watch the video below.
- Center Constraint: Keeps the object centered within the frame, both horizontally and vertically, ensuring it stays perfectly centered as the frame changes size.
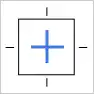
Watch the video below.
- Top, Bottom, Left, Right Constraint: Pins the object to all four sides of the frame, causing it to stretch or shrink with the frame, maintaining its relative size and position.
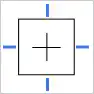
Watch the video below.
- Scale (No Constraint): Allows the object to scale with the frame, maintaining its proportions relative to the frame size, which is useful for background images or large elements.
Watch the video below.


