Advanced Interaction Settings in Figma

Figma's advanced interaction settings empower designers to create dynamic, responsive prototypes that closely mimic real-world user interactions. This guide delves into complex interactions such as sidebar overlays, fixed-position scrolling, and advanced animation techniques. By mastering these tools, you can craft user experiences that are both immersive and intuitive, elevating your prototypes to the next level, whether you’re designing for web, mobile, or beyond
In this section, we’ll cover the following topics.
- Sidebar Overlay
- Fixed Position Scroll
- Horizontal Scroll
- Other Figma Prototype Techniques
Sidebar Overlay
Overlays are a common feature in modern UI design, often used for opening sidebars, modal windows, or pop-ups. Figma simplifies the process of creating these overlays with its intuitive Open overlay interaction setting.
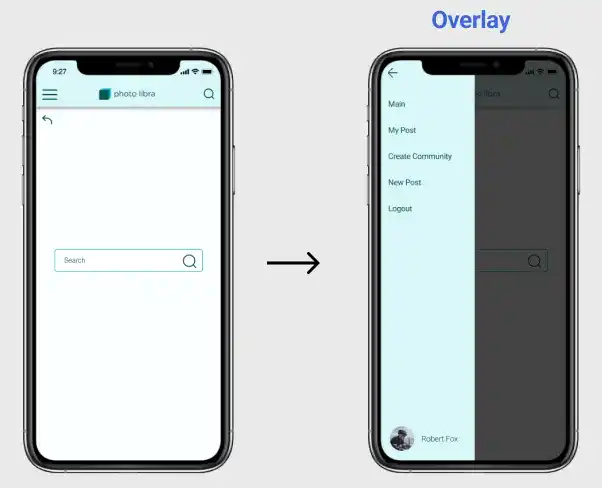
How to Set Up an Overlay:
- Select the Open Overlay Event: Start by selecting the element that will trigger the overlay (e.g., a menu button) and choose the Open overlay event in the interactions panel.
- Choose the Overlay Frame: Specify the frame that you want to open as the overlay. This could be a sidebar, modal, or any other content you wish to overlay on the current screen.
- Positioning: You can position the overlay relative to the current frame. Options include aligning it to the top, bottom, left, or right, or centering it on the screen.
- Close on Click Outside: Enable this option to allow users to close the overlay by clicking outside of it, which enhances usability by offering an easy way to dismiss the overlay.
- Background Settings: Adjust the background color or opacity of the underlying screen when the overlay is active. For example, darkening the screen can draw more attention to the overlay.
- Animation Effects: Add animation effects to make the overlay appear more fluid. For instance, you can have the sidebar slide in from the left or fade in smoothly.
Subscribe now for
uninterrupted access.